• In-situ crystallization of APIs within the carrier achieves process integration.
• The process obviates requirement for high-energy equipment.
• Particle dispersion is achieved through droplets generated by LLPS.
• The ND@SLMs feature high drug loading,low toxicity,and uniform dispersion.
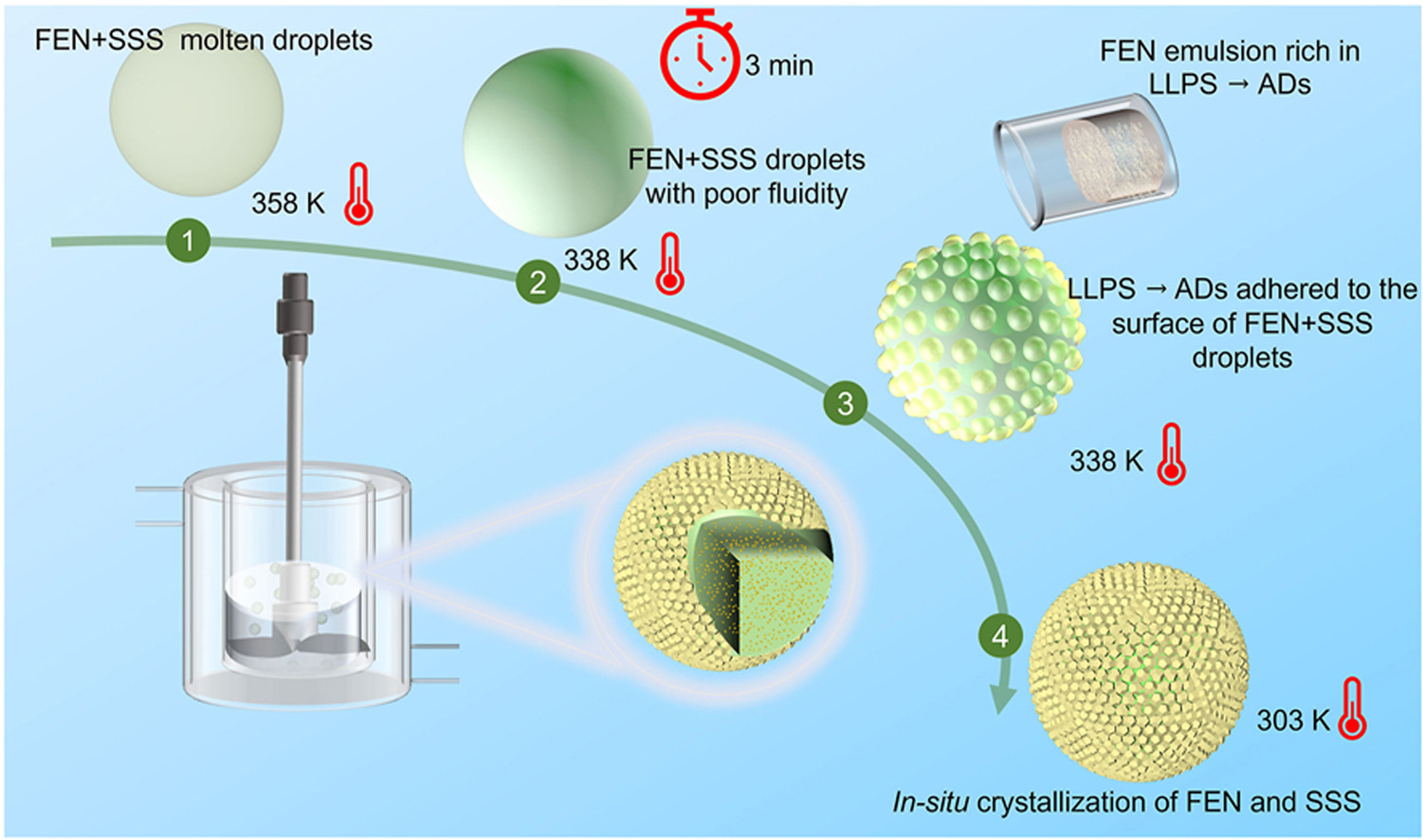
In this work,API nanoscale drugs loaded onto solid lipid microspheres (ND@SLMs) were successfully prepared by combining in-situ crystallization technology and liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS). This method is characterized by its low energy consumption and the absence of a requirement for high concentrations of surfactants. Tristearin (SSS) was used as the drug carriers,and fenofibrate (FEN) was used as API to verify the feasibility of this method. Characterization was performed using SEM,PXRD, and DSC, while in-situ Raman and EasyViewer enabled real-time monitoring of the particle formation process. The results show that the obtained Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) nanoscale crystals exhibited uniform distribution in the solid lipid carrier and enhanced release rates compared to the bulk ingredients. API droplets prepared by LLPS adhered to the surface of the FEN + SSS droplets played the role of dispersant. Response surface analysis was employed to analyze the independent variables and their interactions, and the optimum value of the processing parameters was obtained. Finally,the expandability of this method to other hydrophobic drugs was verified by ibuprofen (IBU).