• High-purity alumina particles was fabricated for the first time by spray drying method.
• SDS modification of Al2O3 surface significantly enhanced methylene blue (MB) removal.
• Sorption capacity value of SDS-modified Al2O3 (SA) for MB is 60.99 mg/g.
• Adsorption of MB onto SA is mainly driven by electrostatic interactions.
• Adsorbent can be reused after 5 cycles with a removal efficiency of 83.96 %.
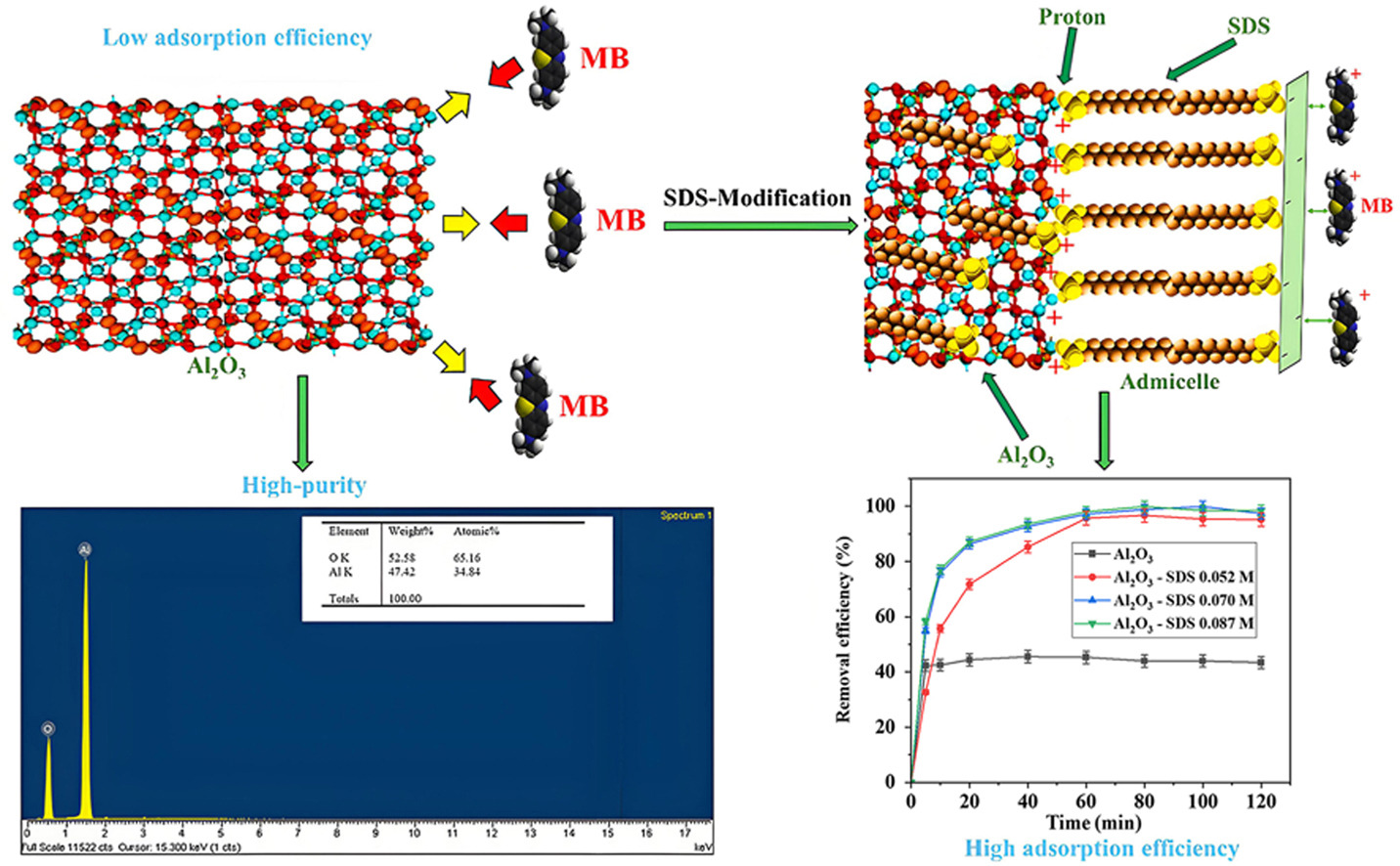
In the present paper, we facilely fabricated novel high-purity alumina particles with uniform morphology and size distribution by spray drying method. Despite the synthesized alumina's excellent physical characteristics, its interaction with dyes remains low. Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), an anionic surfactant, was chosen to modify the alumina surface for enhanced methylene blue (MB) removal performance. The SDS-modified alumina (SA) adsorbent properties were discovered by utilizing fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), zeta potential, scanning electron microscope (SEM), and nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherms. The favorable conditions for MB removal onto SA including working solution pH, SDS concentration, material dosage, adsorbate concentration, strength of ionic, and temperature were set at 60 min. The MB removal efficiency on SA reached approximately 99 % with a corresponding reaction rate of 0.05 g/(mg min). In addition, the MB adsorption isotherm was illustrated effectively using a two-step sorption model, with a calculated qmax value of 60.99 mg/g. The novel adsorbent exhibited strong adsorption affinity for both MB, Janus Green B (JGB), and Victoria Blue B (VBB). The removal mechanism of MB on SA was thoroughly conferred and supported by FT-IR analysis and zeta potential. Furthermore, the removal efficiency of SA only decreased nearly 15 % after 5 cycles, indicating that the adsorbent exhibited respectable regeneration performance. These results demonstrated that SA is a promising material for the scavenge of wastewaters containing various cationic dyes.