• Mixing characteristics of two typical non-spherical particles in a paddle mixer was studied by DEM.
• DEM models of flat particles and prismatic particles were established based on muti-sphere method.
• Diffusion motion of particles in circumferential direction promoted the axial movement of particles.
• Diffusivity of prismatic particles was higher than that of flat particles.
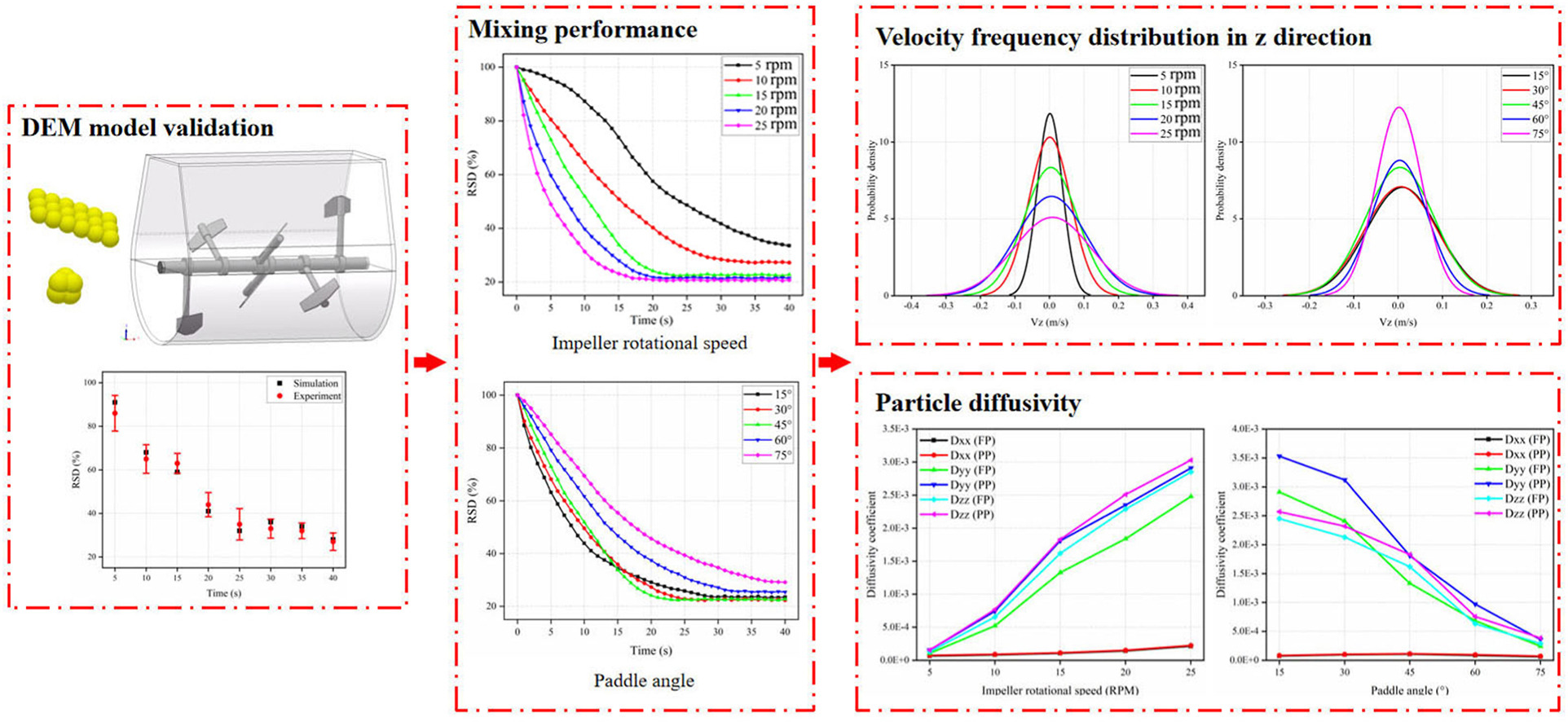
The discrete element method (DEM) and experimental measurements were employed to investigate the influence of impeller rotational speed and paddle angle on the mixing characteristics of two types of non-spherical particles in a paddle mixer. A close agreement between the simulation and experimental data was observed. By analyzing the motion of particles, it was found that a wide range of diffusion motion occurred when the particles pushed by the paddle blades rolled down the surface of the upper flowing layer of particles in the vessel, which caused the strong circumferential motion of particles, meanwhile promoted the axial movement of particles. The mixing characteristics were analyzed using relative standard deviation (RSD), velocity frequency distribution, diffusivity coefficient and Peclet numbers. The mixing process was accelerated at the rotational speeds of 15, 20, and 25 rpm, meanwhile the superior mixing performance was achieved at the paddle angles of 30° and 45° in the study. The fluidity of particles in circumferential direction was higher than that in axial direction. Diffusion was the prevailing mixing mechanism in the current mixing system.