- Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
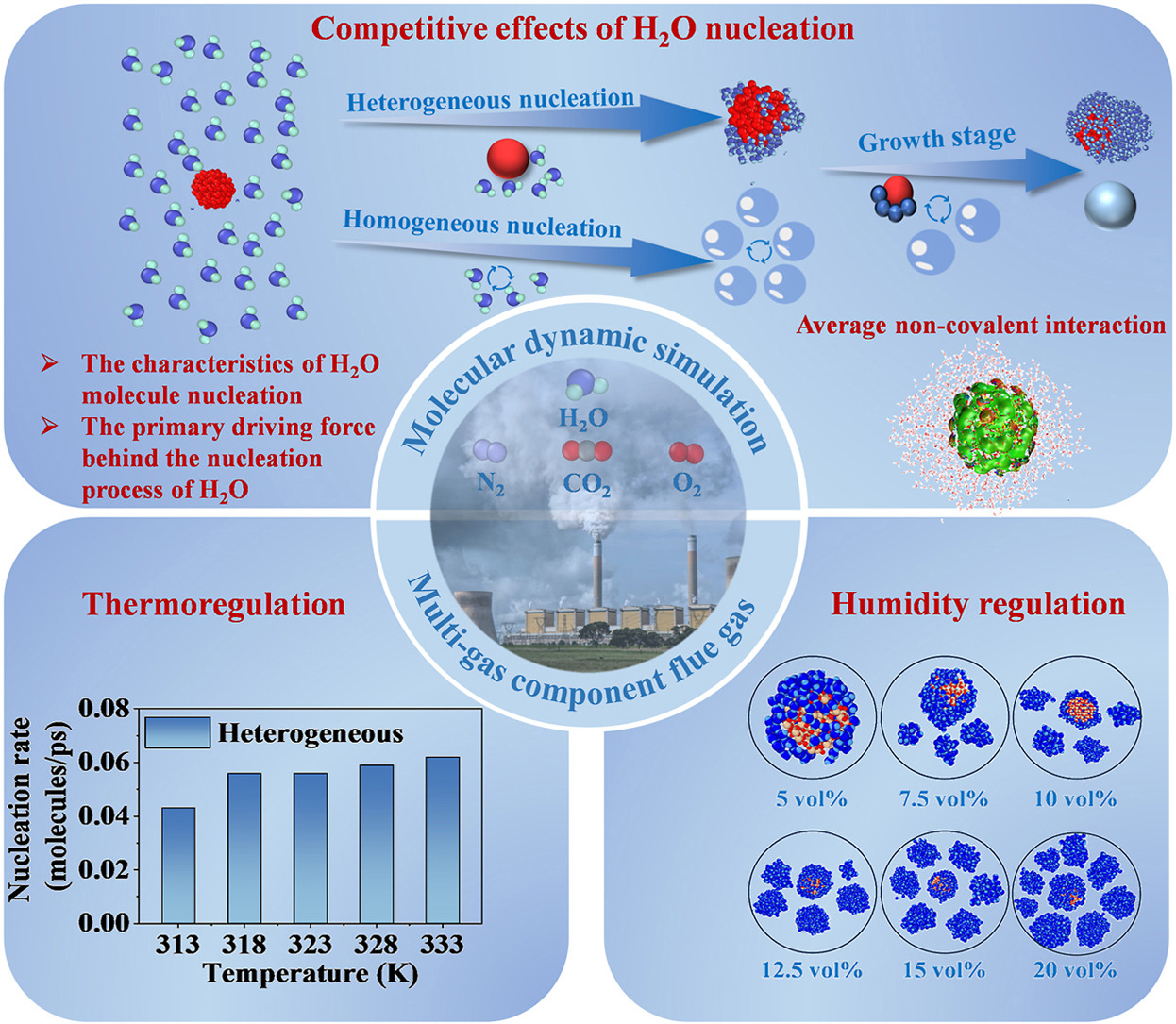
• Molecular dynamics were used to study particle growth in multi-component wet flue gas.
• Nucleation sites were identified during heterogeneous nucleation of H2O on particles.
• Dominant factor of heterogeneous nucleation of H2O on particles was explored.
• Flue gas temperature and humidity were combined to regulate particle growth.
The principal method for improving the removal efficiency of fine particles emitted from coal-fired power plants involves the application of water vapor phase change pretreatment technology. This study utilizes molecular dynamic (MD) simulation to examine the heterogeneous nucleation process between fine particles and H2O under conditions of multi-gas composition. Results showed that the heterogeneous nucleation and the homogeneous nucleation process of H2O occur concurrently, with both processes engaged in a competitive relationship. The nucleation process of H2O on particles is characterized by the formation of specific sites. In these regions, H2O interacts strongly with the O atoms on the particle surface through hydrogen bonding, leading to preferential condensation in the vicinity of these sites. The influence of temperature on particle growth primarily involves interaction and self-diffusion processes of H2O. As the temperature decreases, the size of particles initially increases and then decreases, reaching a maximum at 323 K. In contrast to the effects of temperature change, the influence of H2O content on fine particulate growth is primarily characterized by the competition between homogeneous and heterogeneous nucleation of H2O molecules. These findings, including the nucleation characteristics of fine particles and the influence mechanism of gas temperature and humidity, strengthen the theoretical system of water vapor phase change technology to promote the removal of fine particles from coal-fired flue gas, and provide theoretical support for subsequent process optimization.