- Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
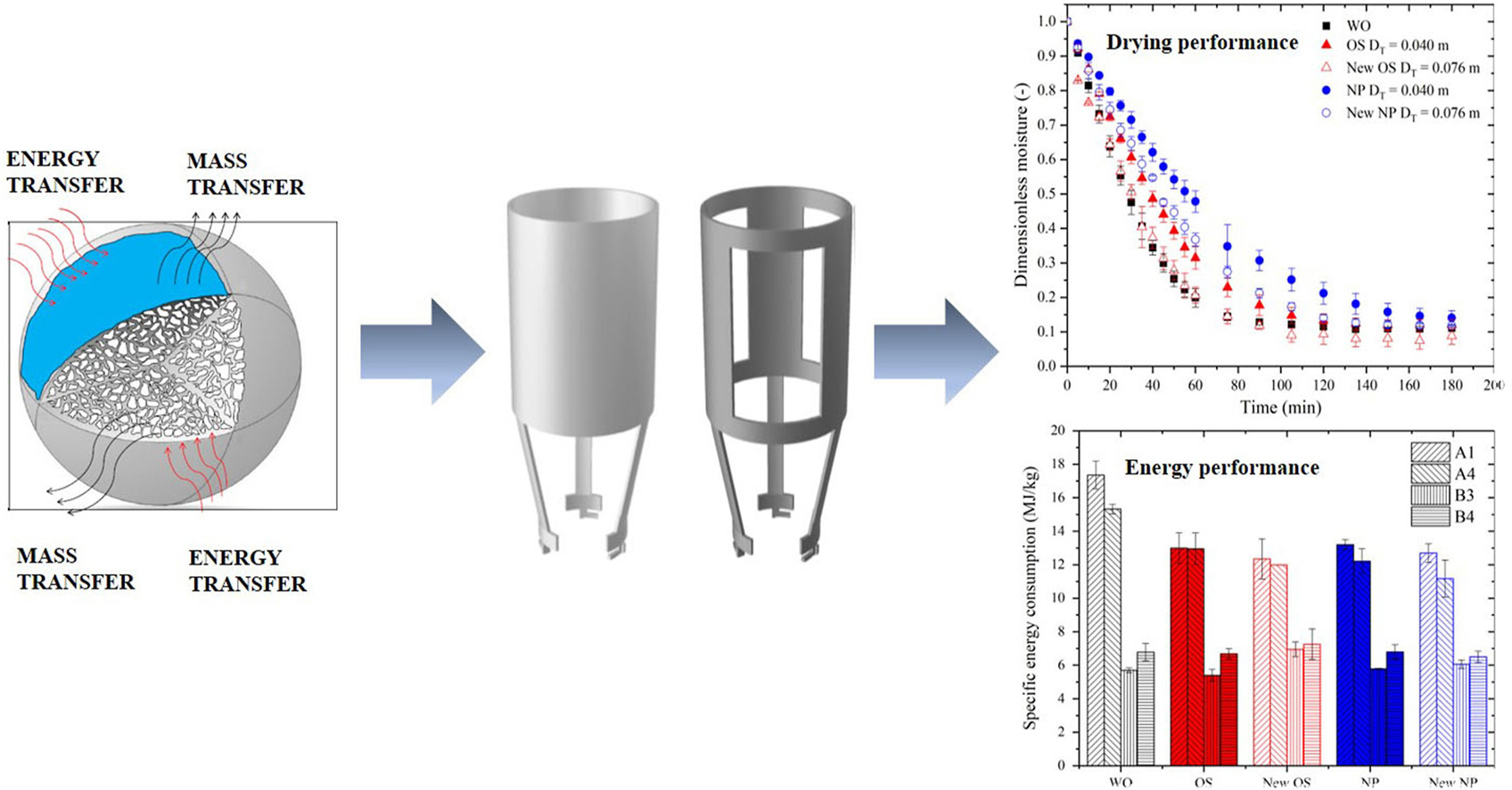
• Novel draft tubes have been assessed to scale up the spouted bed technology.
• Intermittent drying considerably decreases both drying time and energy requirements.
• New open-sided draft tube enhances spouting and drying operation.
Novel draft tubes have been assessed to scale up the spouted bed technology. Accordingly, alumina drying runs have been conducted using different configurations (without tube and with open-sided and nonporous tubes) under intermittent strategies consisting in alternating periods of drying and periods of reduction or interruption of the air flow rate, and they have been compared with continuous drying. Furthermore, the influence the draft tubes have on the drying performance and energy requirements in the drying process has been evaluated. The results allow inferring that intermittent drying considerably decreases both drying time and energy requirements. Moreover, the new draft tubes improved the drying of alumina, as a similar energy efficiency than without draft tube was attained with lower specific energy consumption, which is essential to reduce the high-energy demand in the drying process and mitigate climate change. These findings, along with the stability the new tubes provided to the process, involve a further step in the scale up of spouted beds for industrial operations.