- Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
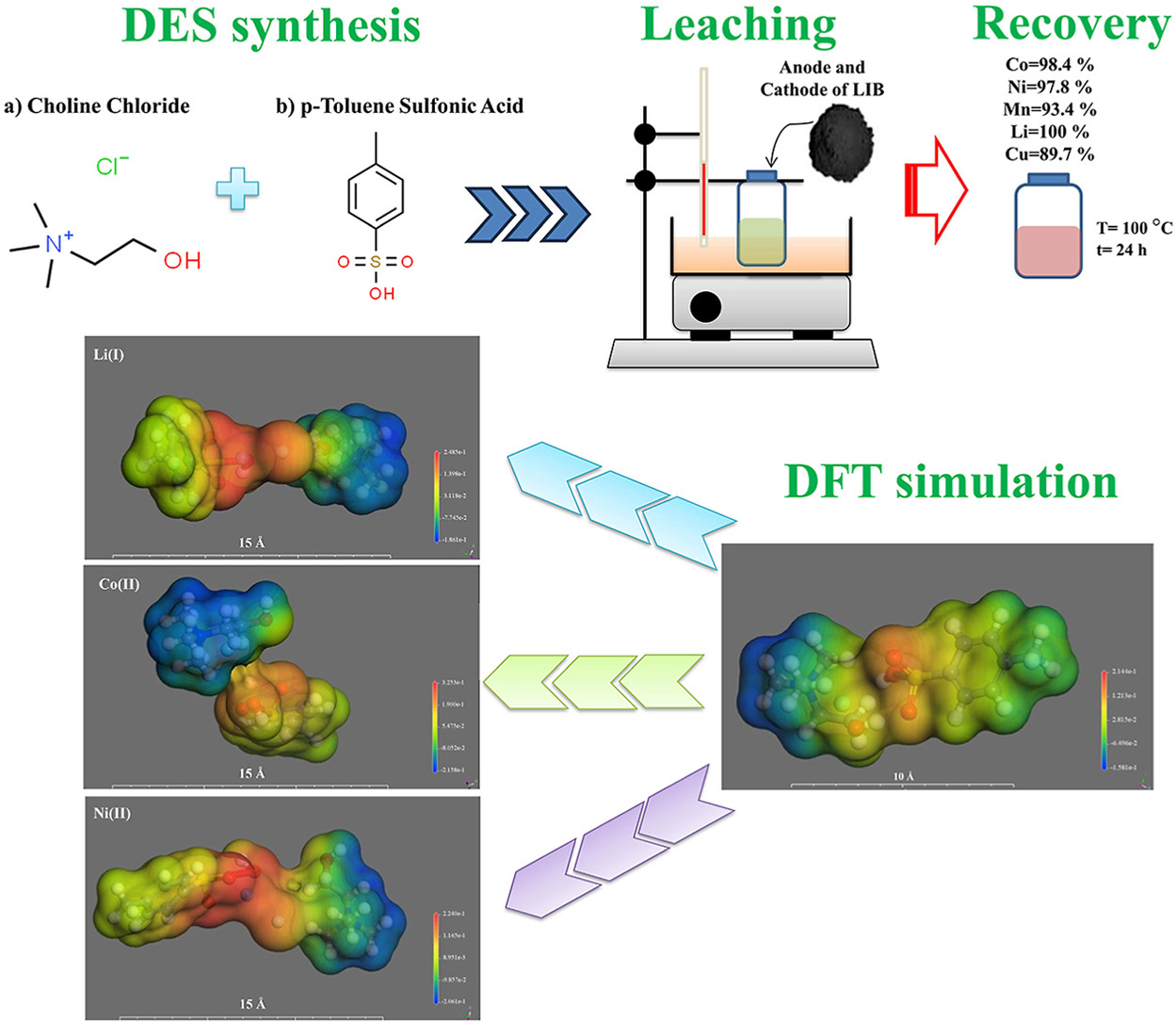
• ChCl-PTSA DES was successfully used for the leaching of LIB A/C.
• Ni, Co, Li, Mn, and Cu dissolved with over 90 % efficiency at 100 °C and 24 h.
• XRD and SEM analyses confirmed the presence of graphite in the leaching residue.
• DFT analysis showed that hydrogen bonding plays a crucial role in the formation of the DES.
• Cu(I), Co(II), and Mn(II) exhibit enhanced stability in the DES system due to high HOMO-LUMO gaps.
In this study, the cumulative dissolution of the anode and cathode (A/C) mixture of Li-ion batteries (LIBs) in a deep eutectic solvent (DES) composed of choline chloride (ChCl) and p-toluenesulfonic acid (PTSA) was evaluated within a temperature range of 40–100 °C and a time range of 20–1440 min. The results showed that Ni, Co, Li, Mn, and Cu metals dissolved with over 90 % efficiency at 100 °C and 1440 min, while Al dissolved at only about 26 % under the same conditions. XRD and SEM-EDS analyses confirmed these findings, with minimum residual compounds of Ni, Co, Li, Mn, or Cu detected. FTIR confirmed ChCl−PTSA DES formation and its after-leaching stability, allowing reuse with minimal changes for sustainable metal recovery. The ChCl–PTSA DES exhibits a symmetric σ−profile (centered at σ = 0 ± 0.2 e/Å2), COSMO-identified nucleophilic/electrophilic regions (+0.214 to −0.158 e/Å2), and Mulliken charges (O: −0.47 to −0.65, Cl: −0.39, H: +0.06 to 0.15). These density functional theory (DFT) simulations highlight charge complementarity, stabilizing the eutectic structure via sulfonic oxygen, chloride, and ammonium group interactions. According to DFT simulation for pure and containing metal ions DES, the ChCl−PTSA exhibits a 3.87 eV HOMO−LUMO gap, enabling efficient metal leaching. Co(II) (2.29 eV gap) and Mn(II) (0.56 eV) show higher stability than higher oxidation states, while Li(I) widens the gap (3.97 eV), enhancing stability. DFT simulations reveal distinct COSMO surface charge distributions for metal ions in ChCl–PTSA, categorized as: (1) highly polarized (Co(II): +0.3253 to −0.2158 e/Å2; Mn(II): +0.3769 to −0.2496 e/Å2), exhibiting strong charge separation and high reactivity; (2) moderately polarized (Ni(II): +0.2240 to −0.2061 e/Å2; Al(III): +0.2547 to −0.2192 e/Å2), balancing reactivity and stability; and (3) minimally perturbed (Li(I): +0.2485 to −0.1861 e/Å2; Cu(I): +0.3233 to −0.1876 e/Å2), showing stable charge delocalization.