• The 4-Bromopyrazole self-assembly behavior is studied by experiment and molecular simulation.
• The 4-Bromopyrazole nucleation kinetics is studied based on solution chemistry and DFT calculation.
• A mechanism is proposed to unveil relation between molecular assembly and nucleation kinetics.
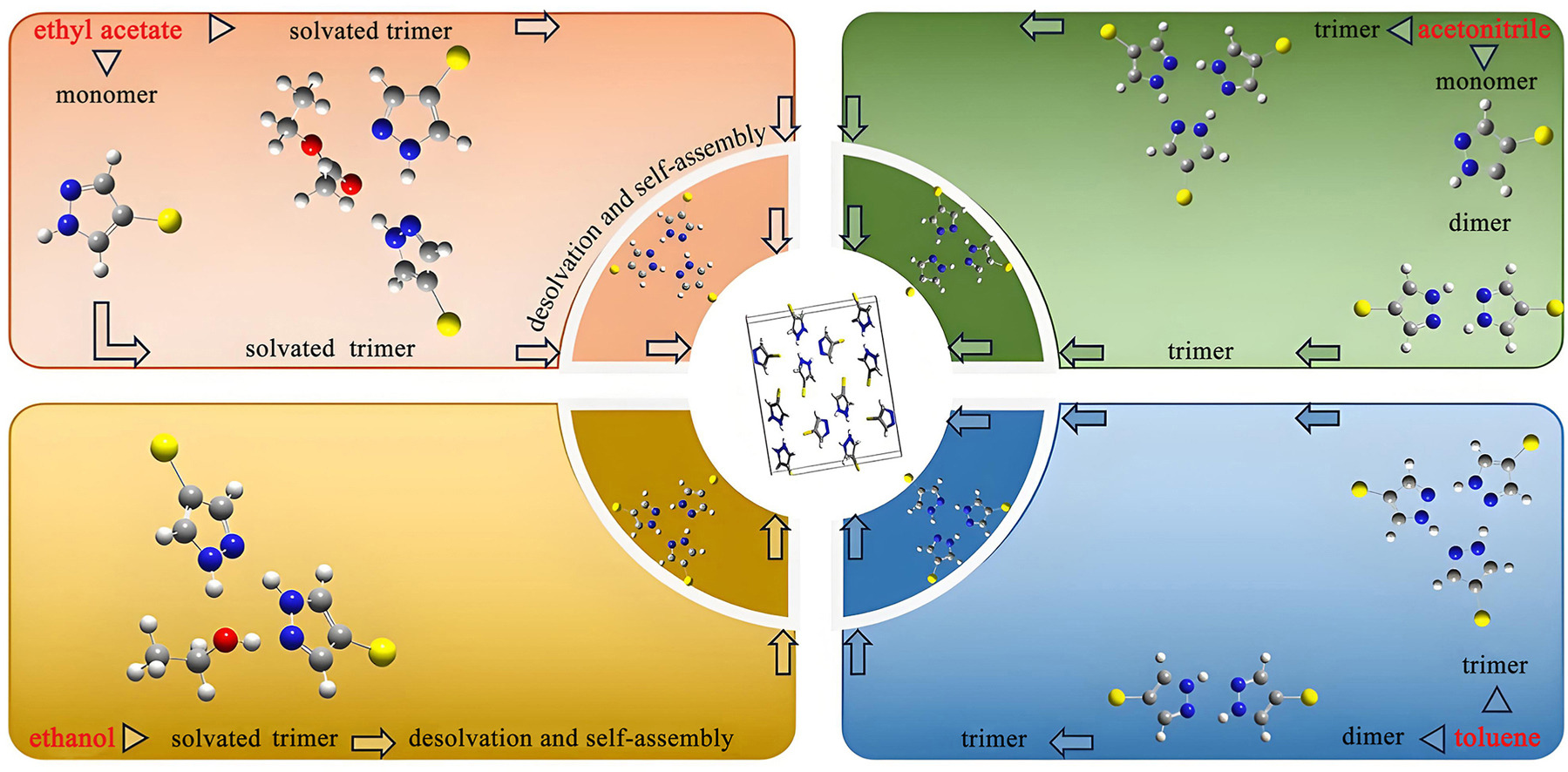
Nucleation is a critical stage during the crystallization process, determining the attributes of the crystalline products. Due to the complicated and microscopic characteristics of the molecular assembly process, the nucleation mechanism has not yet been fully comprehended. In this study, the molecular self-assembly of 4-bromopyrazole (BMPZ) in various solvents and its relation with nucleation kinetics were investigated by the experiment and molecule simulation. Firstly, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, and mass spectroscopy were employed to explore and determine the existed forms of BMPZ molecules in solution. It was unveiled that the BMPZ molecules assembly behavior showed an individual feature. Afterward, the nucleation kinetics was determined by statistical probability distribution method, and the parameters associated with the nucleation process were derived from classical nucleation theory, further associating with the nucleation kinetics. Solution chemistry, molecule simulation, and nucleation kinetics exposed that BMPZ assembly forms could act as the growth unit of the nucleation, and nucleation kinetics was chiefly governed by the interface-transfer process.