• Experimental investigation of rheology of drilling muds containing single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNT) was conducted.
• Influence of SWCNT additives on cuttings transport performance and pressure loss in boreholes was studied.
• Influence of numerous factors on efficiency of particle transport in modified drilling fluids was investigated.
• Efficiency of cuttings transport increases significantly with increasing additive concentration.
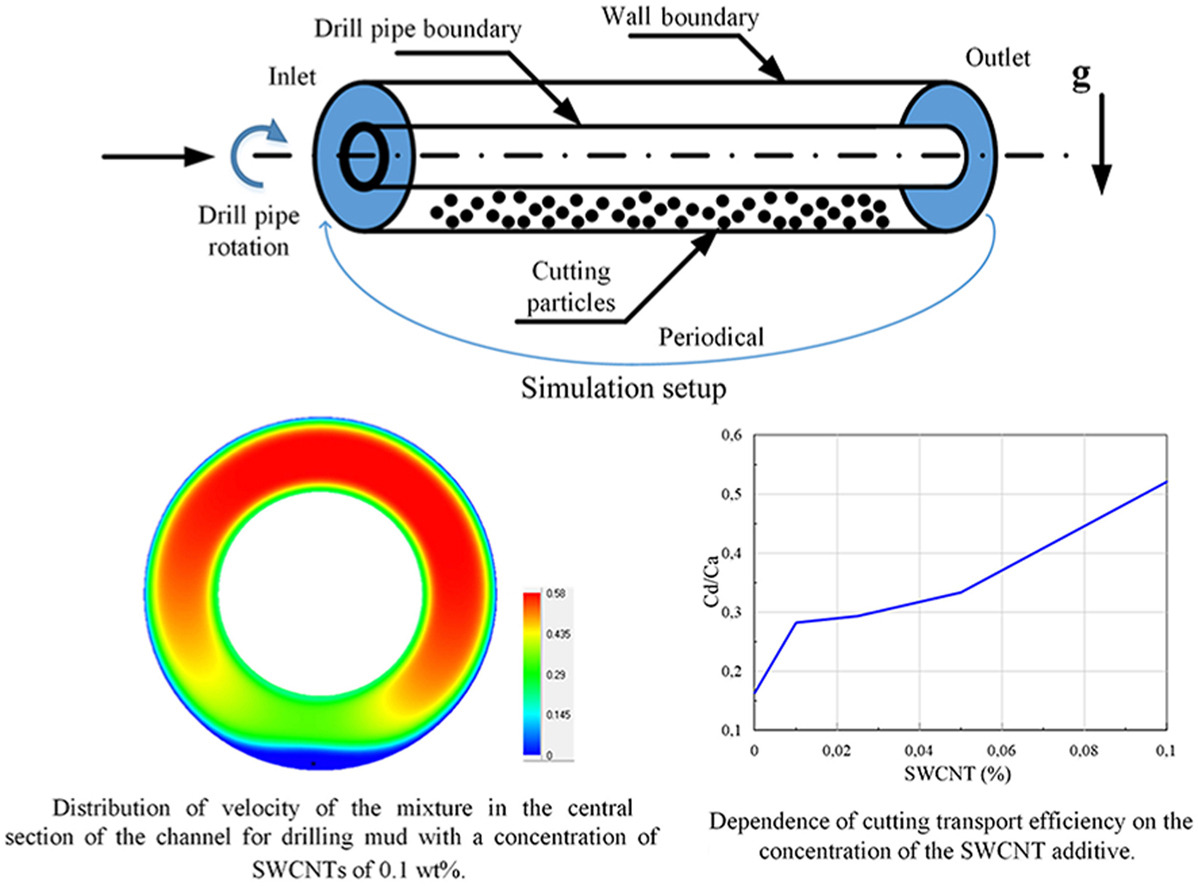
A systematic numerical investigation of slurry transport by drilling fluids modified with single-walled carbon nanotube (SWCNT) additives under laminar flow conditions of the suspension has been conducted. Across wide-ranging parameter variations corresponding to real wells and drilling modes, the effects of the mass flow rate of the drilling fluid, particle size of the slurry, ratio of inner to outer pipe diameters, eccentricity, rotational speed of the inner pipe, and well inclination angle on the efficiency of slurry particle transport by the modified fluids were examined. The influence of the additives on the concentration distribution of slurry particles and the velocity of the mixture in the annular channel, simulating the well, was studied. Mechanisms of the nanotubes' influence on slurry particle transport were identified. It was demonstrated that for all considered cases, the efficiency of particle transport by drilling fluids modified with nanotubes significantly increases with increasing additive concentration. The greatest effectiveness for improving wellbore cleaning was exhibited by a drilling fluid with an SWCNT concentration of 0.1 wt%. For this fluid, the ability to transport slurry increased by a factor of 3.4, while the pressure drop increased only by a factor of 1.8 compared to the baseline fluid. Furthermore, the addition of nanotubes was found to be most effective for horizontal wells with concentric pipe placement, at low rotational speeds of the drill pipe, and at high mass flow rates of the drilling fluid.