• Spreader geometry effect on powder bed quality over rough surfaces is evaluated.
• Spreaders with smaller tilt angles can significantly improve powder bed density.
• Arc-shaped spreaders can improve packing density and distribution uniformity.
• R1000 and half-roundblade spreaders perform best at high spreading speeds.
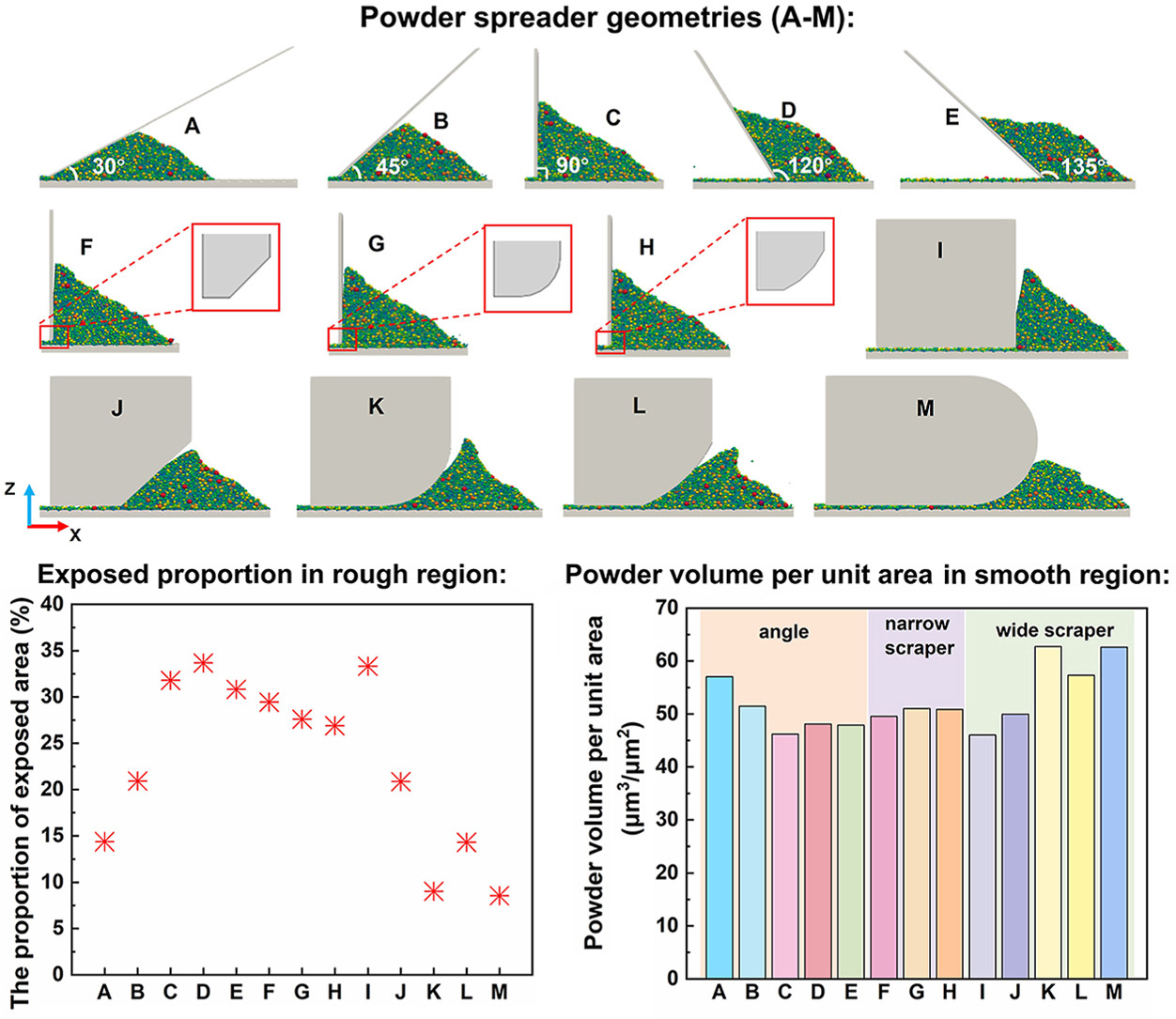
The quality of parts manufactured by laser powder bed fusion is closely related to the uniformity and density of the powder bed. In this work, the discrete element method is used to simulate the powder spreading process by different spreader geometries with rough substrate surfaces. The results indicate that reducing the spreader inclination angle significantly increases the number of force chains, enhances compaction, and consequently improves the quality of the powder bed. Studies also show that optimizing the bottom structure of the spreader can effectively reduce exposed areas. An arc-shaped structure promotes particle packing and filling, improving the powder distribution characteristics. A narrow spreader significantly affects the packing density of the powder bed at low layer gaps, whereas a wide spreader is relatively less constrained. At high spreading speeds, the spreader with an inclination angle of 135° produces the highest quality of the powder bed. R1000 performs excellently at larger layer gaps. The above findings provide valuable guidance for optimizing powder spreading strategies in the laser powder bed fusion process.