-
Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volume 105
-
Volume 104
-
Volume 103
Pages 1-314 (August 2025)
-
Volume 102
Pages 1-276 (July 2025)
-
Volume 101
Pages 1-166 (June 2025)
-
Volume 100
Pages 1-256 (May 2025)
-
Volume 99
Pages 1-242 (April 2025)
-
Volume 98
Pages 1-288 (March 2025)
-
Volume 97
Pages 1-256 (February 2025)
-
Volume 96
Pages 1-340 (January 2025)
-
Volume 105
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
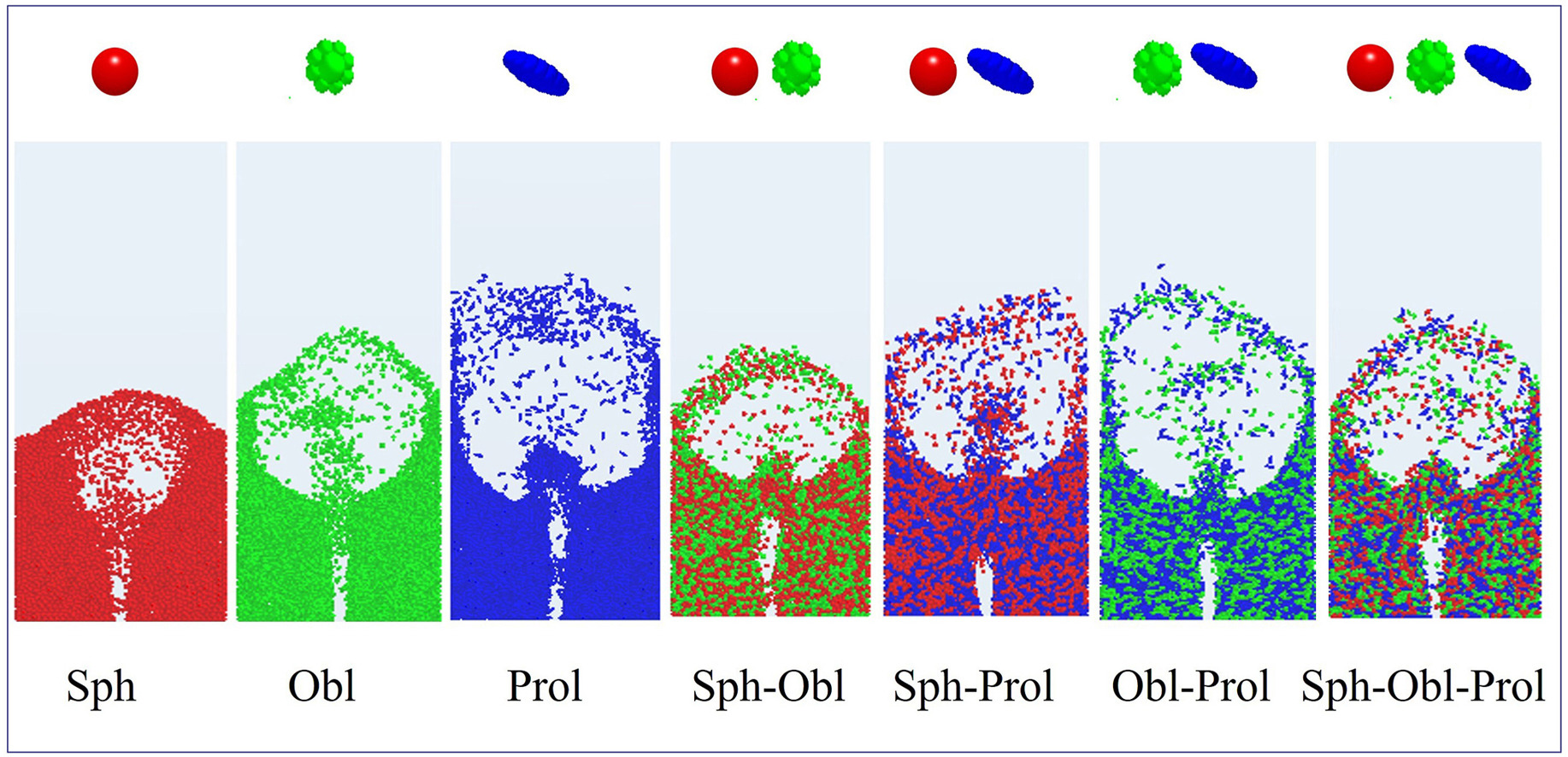
• Spouting behaviors of non-monodisperse systems are studied by CFD-DEM.
• Mixture of spheres and ellipsoids, which is rarely studied in prior similar studies, is considered.
• Three binary mixture and one ternary mixture systems are included.
• Particle shape has important influence on particle behaviors in the spouted bed.
• Altering components for non-monodisperse systems greatly affects spouting behaviors.
Spouted bed is a type of fluidized bed that has been widely used in various industrial processes because of its excellent mass and heat transfer efficiency. In practical applications, the fluidization of the multicomponent particle system containing non-spherical particles is frequently encountered in spouted beds. To better understand the spouting behaviors of the multicomponent particle system, therefore, this study employs a CFD-DEM (Computational Fluid Dynamics-Discrete Element Method) coupling approach to investigate the spouting behaviors. Spherical particles along with two types of ellipsoidal particles (i.e., oblate ellipsoid, and prolate ellipsoid) are included in this paper. Through the combination of these three particle types, seven distinct systems (three monodisperse systems, three binary mixtures, and one ternary mixture) are simulated to analyze the effects of particle shape and composition of particle systems on spouting behaviors. The simulation results reveal that introducing non-spherical particles into systems containing either spherical or oblate ellipsoidal particles tends to enhance spouting behaviors, whereas adding spherical particles to prolate ellipsoidal particle systems inclines to suppress it. The addition of non-spherical particles into the spherical particle system can enhance the particle interlocks, and using the oblate particles should have more important influence than prolate particles. Moreover, the influence of particle shape on the spout deflection behaviors is quite complicated, and the use of prolate ellipsoidal particles versus oblate ellipsoidal particles may produce opposite effects. These findings should provide valuable insights for optimizing spouted bed operations involving complex particle mixtures.