- Volumes 108-119 (2025)
-
Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volume 107
Pages 1-376 (December 2025)
-
Volume 106
Pages 1-336 (November 2025)
-
Volume 105
Pages 1-356 (October 2025)
-
Volume 104
Pages 1-332 (September 2025)
-
Volume 103
Pages 1-314 (August 2025)
-
Volume 102
Pages 1-276 (July 2025)
-
Volume 101
Pages 1-166 (June 2025)
-
Volume 100
Pages 1-256 (May 2025)
-
Volume 99
Pages 1-242 (April 2025)
-
Volume 98
Pages 1-288 (March 2025)
-
Volume 97
Pages 1-256 (February 2025)
-
Volume 96
Pages 1-340 (January 2025)
-
Volume 107
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
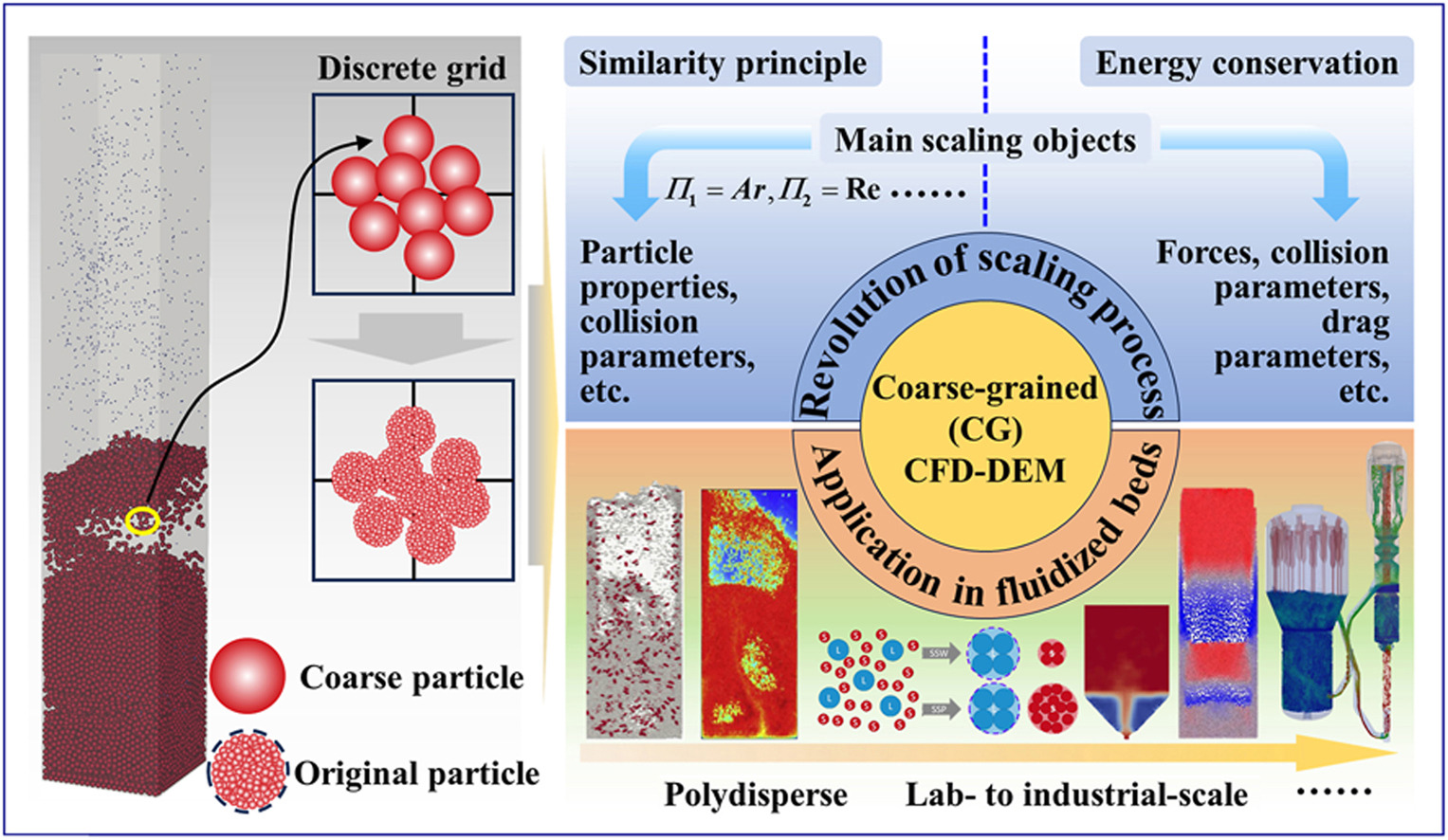
•Revolution of coarse-grained (CG) CFD-DEM based on two principles was reviewed.
•Application of CG CFD-DEM in fluidized beds was comprehensively summarized.
•Some potential drawbacks and critical challenges in CG CFD-DEM were emphasized.
•The CG CFD-DEM simulation for industrial-scale systems is increasingly prominent.
Due to their superior mixing and heat transfer capabilities, fluidized beds are extensively utilized in chemical engineering, power generation, etc. Numerical simulations have long been essential for elucidating the nonlinear multiphase transfer processes within reactors. However, as the research perspective expands from lab-to pilot- and industrial-scale, the exponential increase in particle numbers constrains the applicability of multiphase flow models such as discrete element method (DEM), direct numerical simulation, etc. As an extension of traditional DEM methods, the coarse-grained (CG) DEM strategy effectively balances computational efficiency and accuracy. In order to promote the advancement of CG DEM in the field of fluidized beds, its development and applications are comprehensively reviewed in this work. First, the foundational principles of the CG method—similarity and energy conservation—are outlined. The scaling paradigms of the collision parameters, force formulations, and gas-solid properties are systematically listed in chronological order. Subsequently, the applications of the CG method across lab-, pilot-, and industrial-scale fluidized beds under both cold and heated conditions are summarized. Finally, future challenges and opportunities are highlighted. This review aims to accelerate the adoption of CG techniques in industrial-scale reactors while providing theoretical insights for optimizing existing models and developing novel scaling laws.