- Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
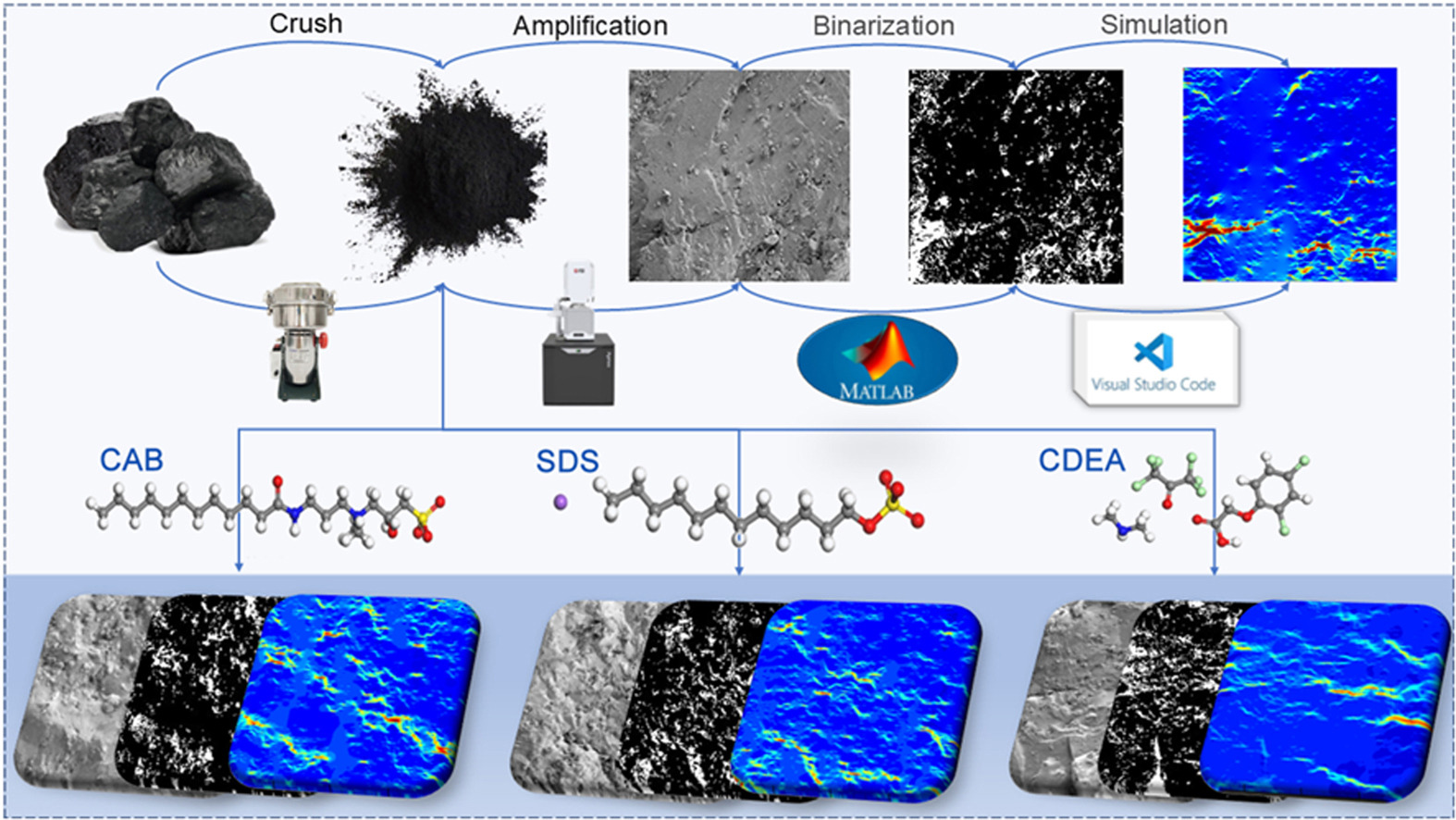
• Microscale digital cores of coal treated by CAB, CDEA, and SDS were reconstructed.
• With the water flow, average velocity exhibited the rapid, slow, and steady decline.
• Critical values of pressure difference within surfactants spread out were determined.
• When ΔP surpassed 15.6 MPa, water injection effect of CDEA-treated coal began improve.
To investigate the mesoscopic influence of surfactants on seepage law during water injection in coal seam, this paper innovatively establishes a fluid transport lattice Boltzmann (LBM) model by incorporating the seepage resistance generated from the porous media and external forces, which embodies the impact of wettability degree resulted from cocamidopropyl betaine (CAB), sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), and coconutt diethanol amide (CDEA) reagents at a 0.1% concentration. The main conclusions derived from this investigation are as follows: Firstly, as the lattice number in the X direction increases, the average seepage velocities in coal samples treated by deionized water, 0.1% CAB, 0.1% SDS, and 0.1% CDEA reagents (Nos. 1, 2, 3, and 4) exhibit three distinct stages: rapid decline, slow decline, and steady decline; in comparison to raw coal sample, modified coal samples demonstrate decreases of 20.84%, 33.91%, and 61.70%, respectively. Secondly, the critical values of displacement pressure difference exist during the phenomenon that modified reagents spread out in the entire flow channel, which are 3.5, 3.5, and 5.2 MPa, respectively, for coal samples Nos. 2, 3, and 4; this signifies that surpassing these critical values help prevent issues such as blank belts within the wetting range and insufficient dust control. Finally, at a displacement pressure difference of 0.01 (lattice unit), the average velocity ratios for samples (Nos. 2, 3, and 4) are 0.78, 0.56, and 0.37 (lattice unit), respectively; notably, the water flow velocities in modified coal samples are lower compared to that in raw coal sample, indicating that the addition of surfactants impede the seepage process of water injection in coal seam. Moreover, when the displacement pressure difference reaches 0.03 (lattice unit), the velocity ratio of CDEA-modified coal sample exceeds 100%; this means that when the displacement pressure difference surpasses 15.6 MPa, the water injection effect of CDEA-modified coal sample begins to be improved. These research findings offer a theoretical basis for enhancing water injection technology in coal mines.