- Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
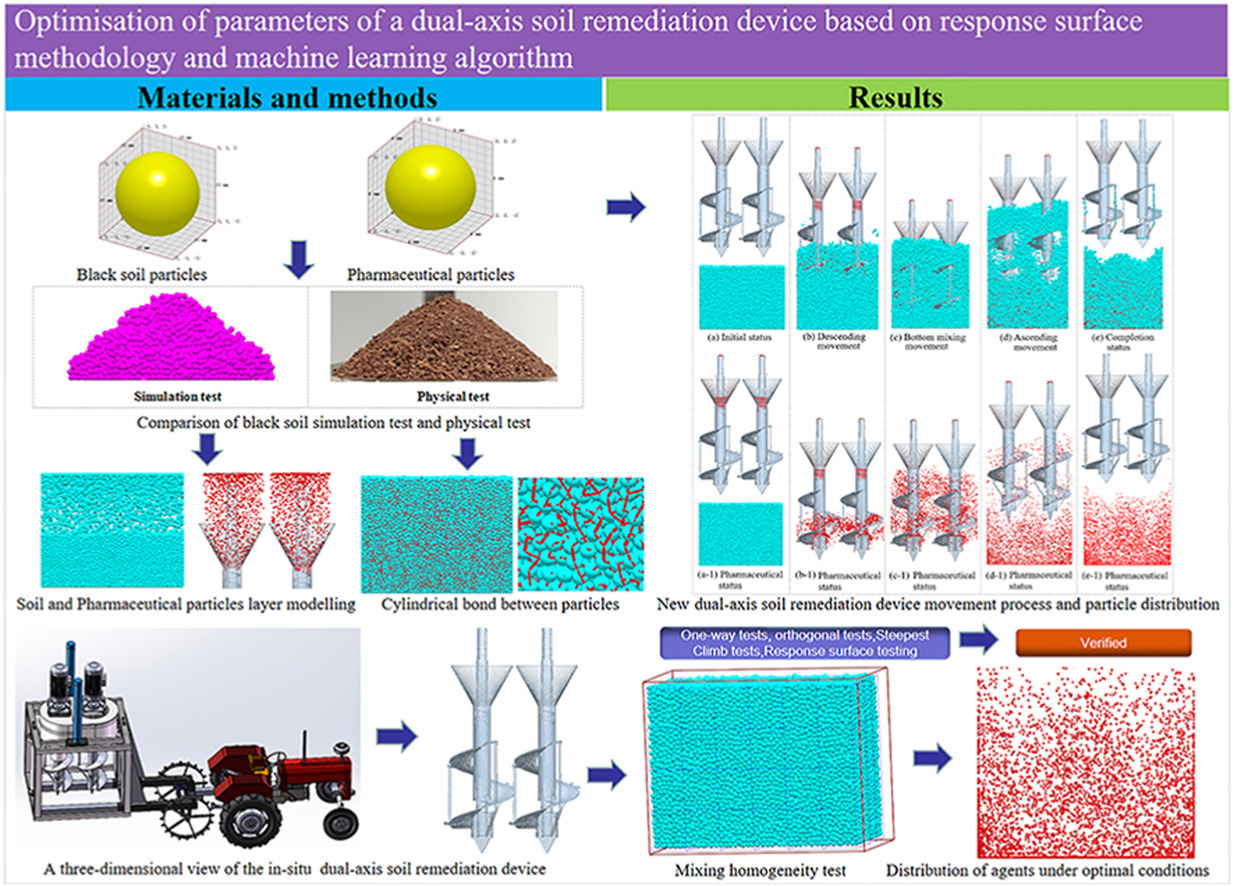
Zhipeng Wang *, Tong Zhu *, Youzhao Wang *, Feng Ma, Chaoyue Zhao, Xu Li, Yanping Zhang
• Machine learning and response surface methodology study of soil-agent mixing characteristics.
• The predictive performance of three machine learning models is compared.
• Improvement of mixing homogeneity in a new biaxial in-situ soil remediation plant.
• Provides reference values for the design of multi-axis soil remediation equipment.
To accelerate the recycling of black soil, it is necessary to develop a new type of soil remediation equipment to improve its working efficiency. The one-way test was used to determine the mean level value of the steepest climb test, and the combined equilibrium method was used to determine the upper and lower interval levels of the response surface test for parameter optimisation. Based on the results of the response surface indices, machine learning was performed and the optimal model was determined. The results show that the predictive ability and stability of the decision tree model for the two indicators are better than that of random forest and support vector machine. The optimal parameter combinations determined using the decision tree model are: speed 73 rpm, homogenisation pitch 183 mm, homogenisation time 1 s, descent speed 0.06 m/s. The error between the optimal value of the machine learning prediction model and the actual simulation is 1.1% and 5.72%, respectively. The results of the study show that the effect of optimizing the parameters through machine learning achieves a satisfactory prediction accuracy.