- Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
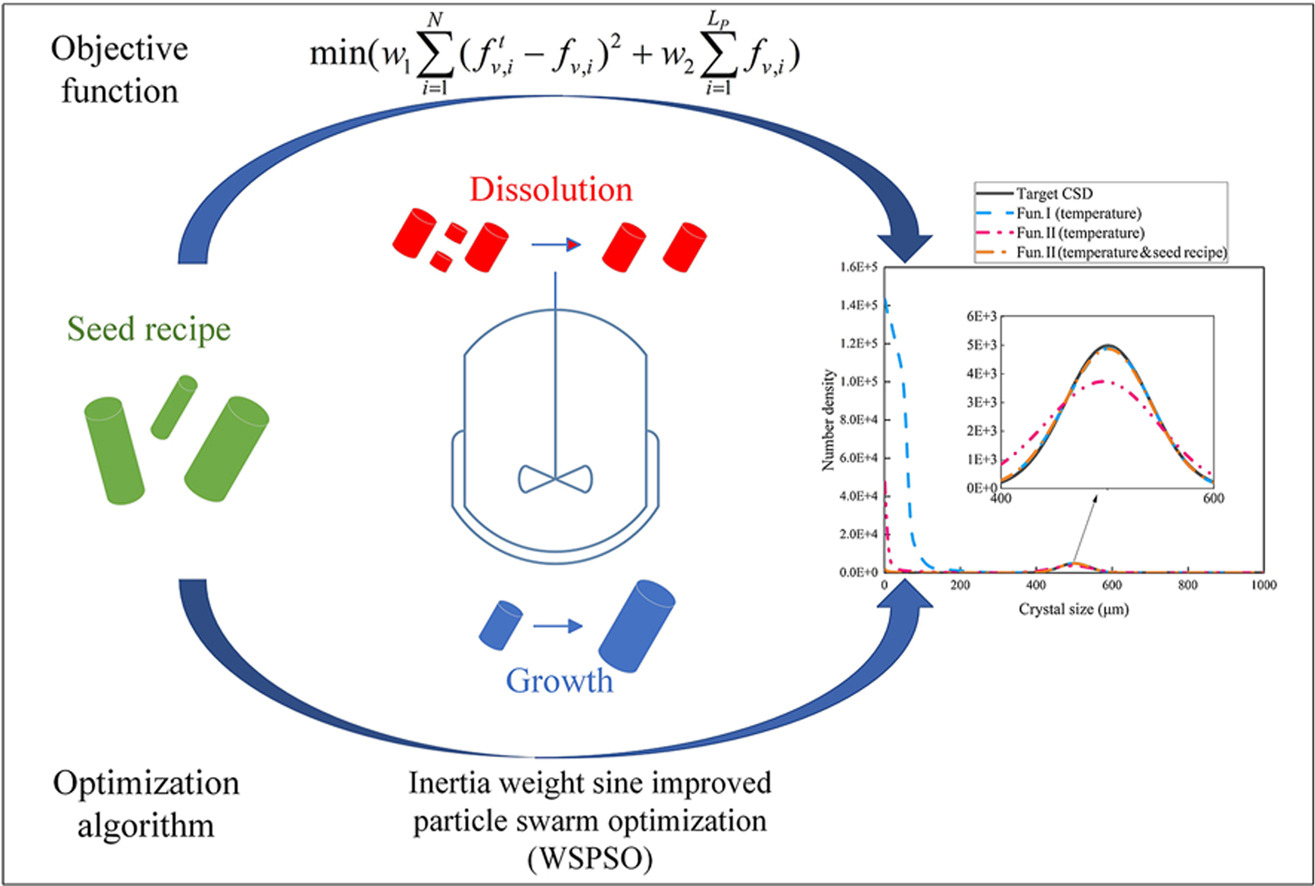
• A new method with new objective function and improved optimization algorithm was proposed for optimal control of CSD.
• Optimal control of CSD with suppressed numerical discrepancy was developed by combining seed recipe and temperature-swing.
• A newly constructed sinusoidal weight function was used to improve the particle swarm optimization algorithm.
• Two cases demonstrated fine crystal mass and number can be reduced by over 90% by the integrated optimization approach.
Optimal control of batch crystallization systems is still a focus and hot topic in the field of industrial crystallization, which seriously affects the consistency of batch product quality. In this paper, a new method with a new objective function and improved optimization algorithm was proposed for optimization of crystal size distribution (CSD) in case of fine crystals occurrence. The new objective function was developed with better margin metric and weighting technique to minimize fine crystal mass, meanwhile, a newly constructed sinusoidal weight function was introduced to improve the particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm. A precise control of CSD with suppressed numerical discrepancy caused by fine crystals removal was developed by combining seed recipe and temperature-swing. In addition, the effects of temperature curve segments on CSD during process optimization were systematically investigated to achieve optimal results. Two typical batch cooling crystallization systems were used to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method in controlling product CSD while minimizing fine crystal mass. Results demonstrated that the desired product CSD can be achieved with minor errors while the fine crystals could be shrunk to be negligible, i.e., the fine crystal mass and number can be reduced by over 90%. This work has an important guiding significance for the removal of fine crystals in industrial crystallization processes, especially when only operational optimization rather than equipment updating is considered.