- Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
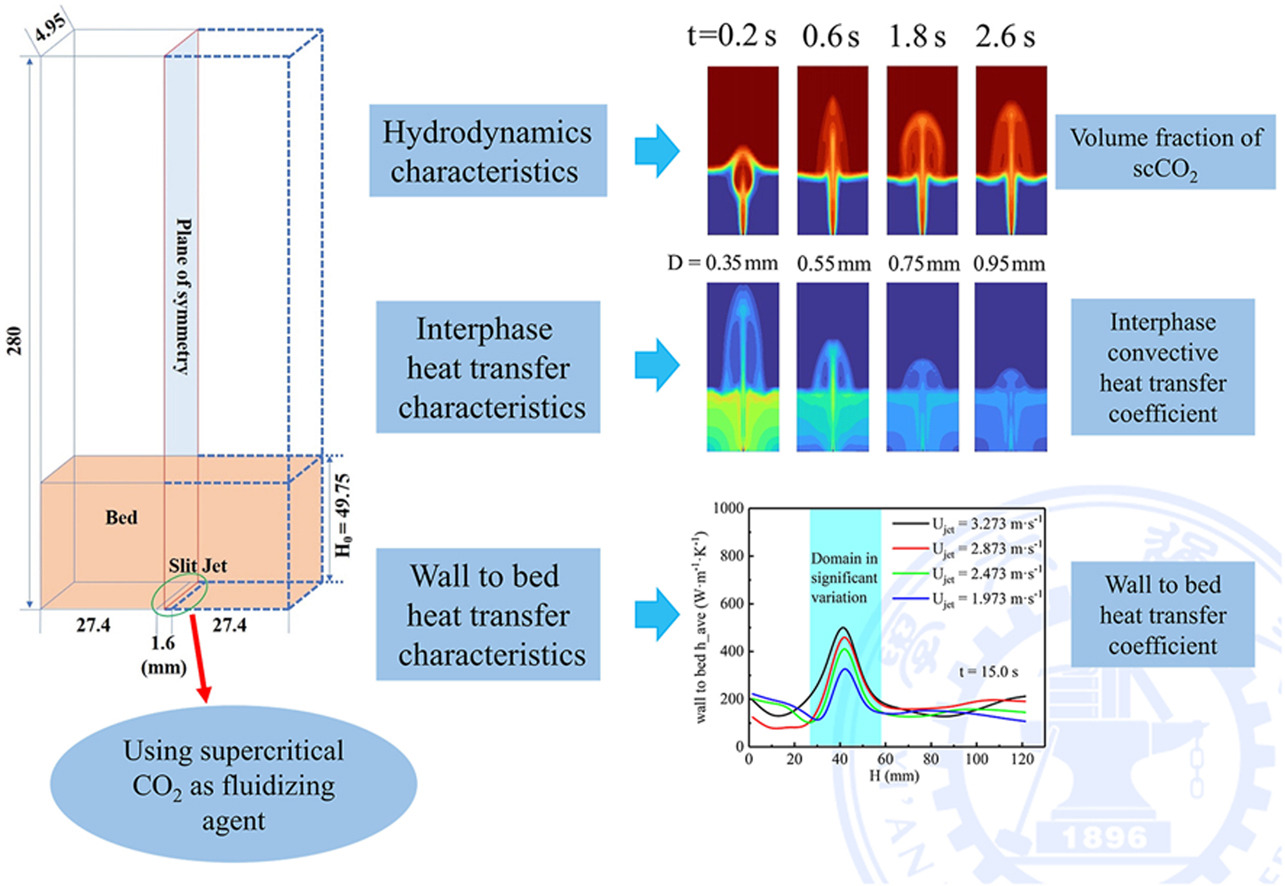
• Larger particle concentration promotes inter-particle collisions while suppress kinetic motion of particles in spout zone.
• Decreasing particle size enhances interphase convective heat transfer coefficient, while increases Ujet results insignificant impacts.
• Transition zone between annular and periphery zone has a certain enhancing effect on wall to bed heat transfer coefficient.
By employing the Eulerian-Eulerian Two Fluid Model, the effect of different particle size, supercritical CO2 (scCO2) velocity at slit jet (Ujet) and initial bed height on the macroscopic characteristics (i.e., fountain morphology, profiles of particle velocity, momentum transfer characteristics among particles, transient temperature evolutions of particles, interphase heat transfer coefficient and wall to bed heat transfer characteristics) in the pseudo 2D rectangular spouted bed using scCO2 as fluidizing agent is numerically studied in detail herein. Considering there are currently no relevant visualized experiments reported using scCO2 as a fluidized agent due to the extreme operating pressure of CO2 (25 MPa in this paper) under supercritical conditions, present numerical model was validated with experimental data by using air as the fluidizing agent, confirming simulated instantaneous volume fraction distribution of air and transient temperature evolutions of particles basically consistent with the experiments. Numerical results reveal some of the internal relations among hydrodynamics characteristics in bed, momentum transfer characteristics among particles and relevant heat transfer behaviours. Results show larger Ujet and smaller particle size will accelerate the particles' translational motion in spout, spout core and fountain core zone. Larger particle concentration will promote inter-particle collisions while suppress the kinetic motion of particles in above zones. Decrease the particle size will enhance interphase convective heat transfer coefficient, while increasing Ujet results insignificant impacts. Finally, we also observe the transition zone between annular and periphery zone has a certain enhancing effect on the wall to bed heat transfer coefficient.