- Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
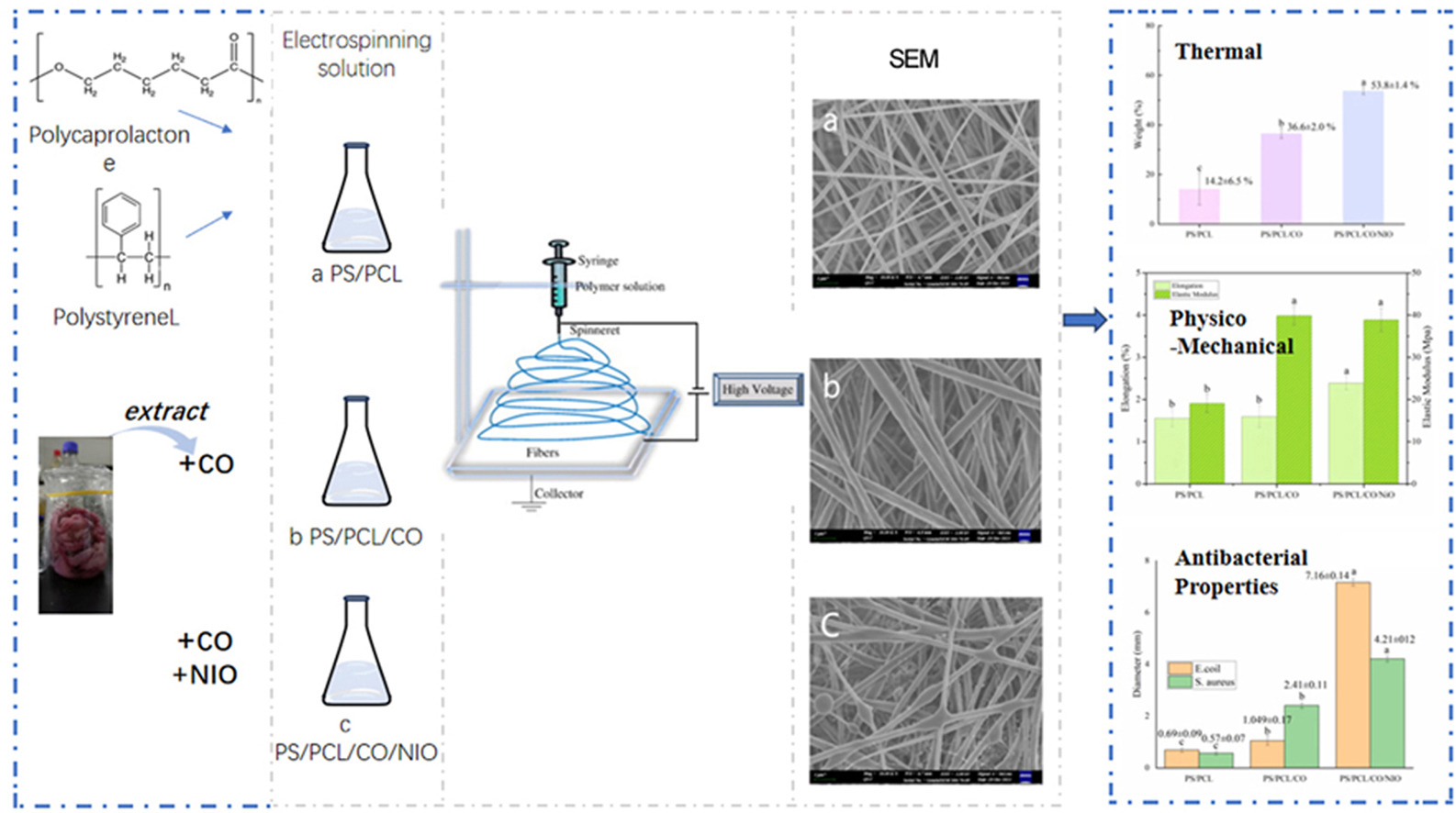
• Squid collagen boosts membrane strength by 86% in electrospinning.
• NiO nanoparticles improved antibacterial activity against E. coli and S. aureus.
• Collagen and NiO improve thermal stability, verified by DSC and TGA.
• The membrane offered controlled release capabilities, suitable for drug delivery.
Electrospinning technology was employed to fabricate a novel composite membrane integrating collagen from Peruvian squid skin with polystyrene (PS), polycaprolactone (PCL), and green-synthesized nickel oxide (NiO) nanoparticles (PS/PCL/CO/NiO). The addition of collagen (CO) and NiO nanoparticles significantly enhanced the membrane's hydrophobicity, as evidenced by an increase in the water contact angle from 124.8 ± 0.6° to 131.2 ± 1.2°. Mechanical properties showed substantial improvement, with tensile strength increasing by 86% (from 5.05 ± 1.6 MPa to 9.39 ± 1.4 MPa) and elongation at break improving by 48% compared to conventional NiO membranes. Thermal analysis indicated increased stability, with a higher endothermic peak and an enthalpy increase from 6.885 J/g to 8.584 J/g. Antibacterial assays revealed strong efficacy against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus, reducing bacterial growth by over 90%. The enhanced hydrophobicity, mechanical strength, thermal stability, and antibacterial activity of PS/PCL/CO/NiO membranes make them highly promising for applications in tissue engineering, wound dressings, and water treatment.