- Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
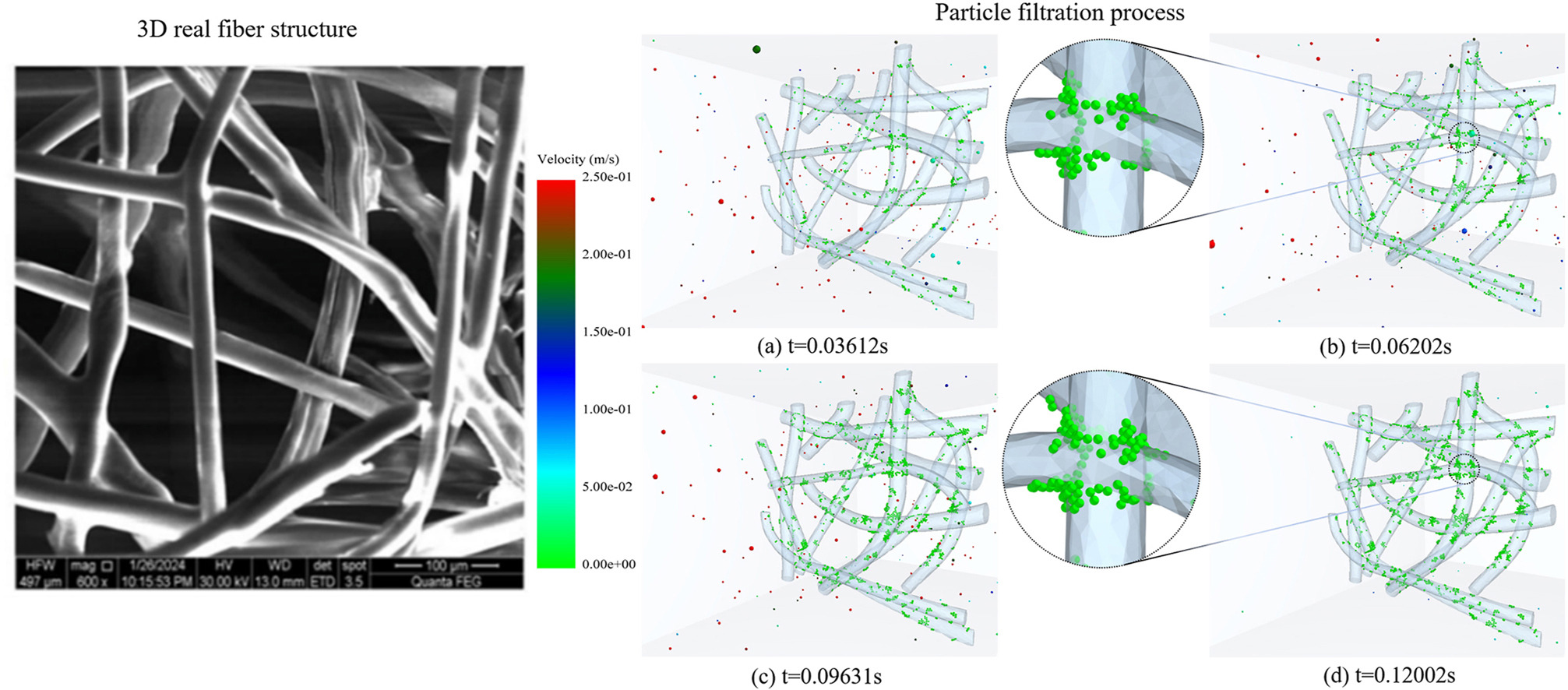
• Model of fibre geometry consistent with real fibre structure is used for particle filtration.
• Particle transport and deposition in fibre media are studied by a coupled CFD-DEM.
• Effect of dimensionless numbers on particle-loaden filtration is explored.
• Inertial impact and interception mechanisms are considered for particle filtration.
• Dynamic filtration performance of fibrous filters is investigated.
In this paper, the particle-loaden filtration of real fibre media was numerically studied using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and discrete element method (DEM) method. The filtration performance was comprehensively analysed by combining fluid and particle properties into a single dimensionless number, Stokes number (St). The results indicated that the capture efficiency increased with St until it stabilised at a certain limit value, which was in good agreement with the results of the previous empirical laws, confirming the accuracy and reliability of the CFD-DEM algorithm. In addition, the capture contribution of fluid and particle properties were investigated. It was found that increasing particle size and density was effective in improving capture efficiency. Moreover, reducing fluid viscosity was the most favourable condition for improving filtration performance. For the dynamic filtration of particle size dp = 2–4 μm, the evolution of the capture efficiency and the pressure drop for dp = 4 μm was higher than that of other particle sizes due to the easy formation of the dendrite structure. In terms of the quality factor, the fibre layer exhibited a better filtration performance for particles with a diameter of 4.0 μm. This study provided a good understanding of dynamic particle-loaden filtration, which is useful for the optimal design of fibre filters.