- Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
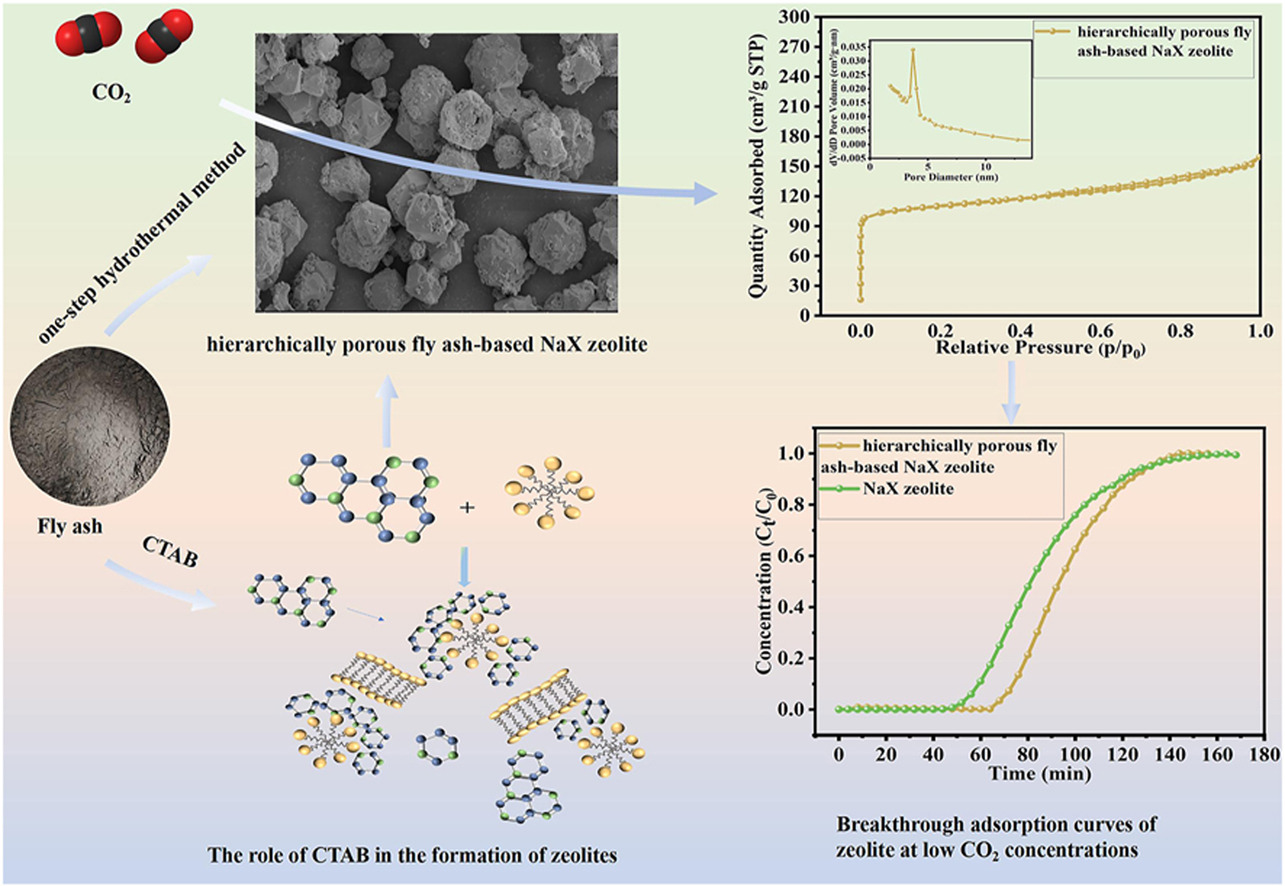
• One-step synthesis of hierarchically porous fly ash-based NaX zeolite for low-concentration CO2 adsorption.
• CTAB assisted synthesis of mesoporous and hierarchically porous zeolites with abundant and controllable mesopore.
• CTAB promotes mesopore formation and inhibits crystal growth during zeolite synthesis.
Despite significant attention being drawn to the synthesis of zeolites from fly ash for CO2 adsorption, few studies have focused on hierarchical porous NaX zeolites derived from fly ash. The existing synthesis methods are often complex, and the role of CTAB in zeolite formation remains unclear. To address these research gaps, we employed a one-step method for synthesizing hierarchically porous fly ash-based NaX zeolites with tunable mesoporosity. Utilizing CTAB as a template agent, we conducted a comprehensive investigation into the effects of varying CTAB dosages and aluminum source types on zeolite formation. The synthesized materials were fully characterized through XRD, FTIR, SEM, TEM, and N2 adsorption/desorption analysis. The results showed that the mesoporous volume of the zeolites can be effectively controlled by adjusting the CTAB/Al2O3 ratio. At an optimal ratio of 0.04, the synthesized zeolite has a surface area of 422 m2/g and a mesoporous volume of 0.116 cm3/g, which represents a two-fold increase compared to the NaX synthesized without CTAB. This improvement of mesoporosity significantly reduces the resistance to CO2 diffusion, thereby enhancing the adsorption performance with a maximum adsorption capacity of 3.37 mmol/g and a high cyclic stability. A further investigation reveals the crucial role of CTAB in promoting mesopore formation and inhibiting crystal growth during zeolite synthesis. These findings provide valuable insights into the one-step synthesis of hierarchical porous zeolites.