• FOX-7/HMX composite crystals were prepared by rotary evaporation.
• Formation mechanism of FOX-7/HMX composite crystals was analyzed.
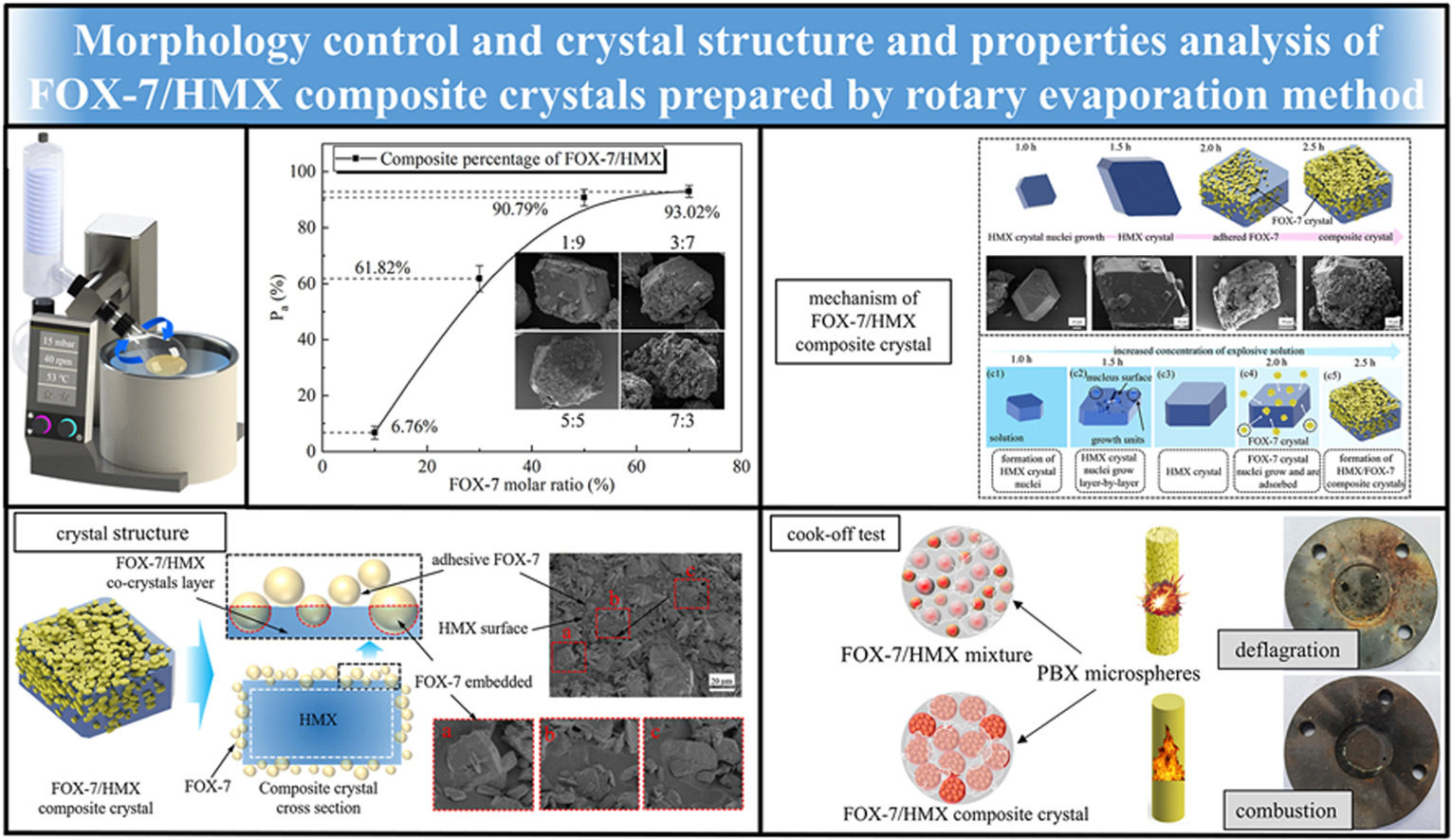
• FOX-7 is embedded on the surface of the HMX crystal, forming a co-crystal layer and changing the crystal structure.
• Composite crystals exhibit elevated thermal stability and impact safety.
Enhancing the safety of high-energy explosives (EMs) is crucial for the secure handling of energetic materials during storage, transportation, and use. Compositing multiple energetic materials effectively enhances the insensitivity of explosives. This study used N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) as a solvent in the rotary evaporation method to prepare 1,1-diamino-2,2-dinitroethene/1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7-tetraazacyclooctane (FOX-7/HMX) composite crystals. By varying the molar ratios of FOX-7 and HMX, this study investigated their effects on the morphology of the composite crystals, and the formation mechanism of the composite crystal was analyzed. The study characterized and tested the crystal structure, thermal decomposition, cook-off performance, and impact sensitivity of the composite crystal. The results indicate that at a 5:5 M ratio of FOX-7 to HMX, the compound degree is 90.79%, and FOX-7 exhibits uniform adhering to the surface of the HMX crystal. FT-IR and XRD patterns analyses revealed shifts in the absorption peak of the composite crystal and the characteristic peak of the XRD curve. FOX-7 crystals were embedded on the surface of HMX crystals, forming a co-crystal layer and altering the crystal structure. Differential scanning calorimetry tests demonstrate that the thermal decomposition temperature of FOX-7/HMX composite crystals is 1.77 °C higher than the raw FOX-7, and during the cook-off test, the composite crystal reaction level is combustion, accompanied by an increase in characteristic drop height to 62.6 cm, indicating improved thermal stability and impact safety.