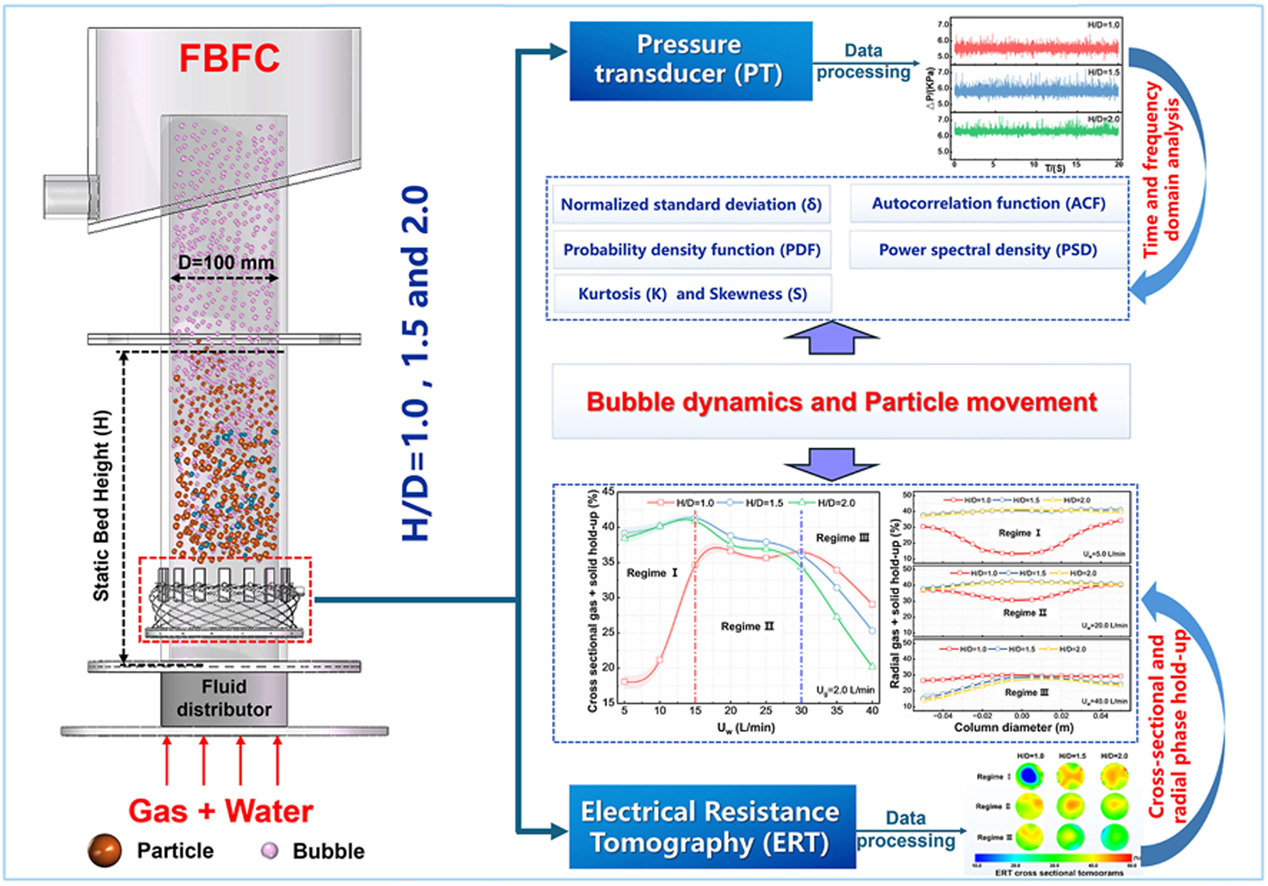
• Static bed height effects on hydrodynamics in fluidized bed were investigated.
• Cross sectional and radial gas-solid hold-ups distribution were detected by ERT.
• Pressure fluctuation signals were analyzed by time and frequency domain methods.
• Bubble dynamics and particle movements cause the variant static bed height effects.
Characterizing the hydrodynamics of a fluidized bed flotation column is essential for understanding the behavior of this multiphase flow system. Bed pressure fluctuations and phase hold-ups are two of these key characteristics. Static bed height effects on these two key characteristics were comprehensively studied using experimental and statistical analysis operating for different flow regimes. And three different bed height-to-diameter ratios (H/D = 1.0, 1.5, and 2.0) were investigated. The time series signals of pressure fluctuation were recorded via a pressure transducer, then analyzed through time and frequency domain methods. Cross-sectional and radial combined gas and solid hold-ups distribution were detected through the electrical resistance tomography under different H/D ratios. Results indicated that the key parameters of bed pressure fluctuation signals and gas-solid hold-up distributions are significantly affected by the change in static bed height, which can be explained by differences in bubble dynamics and particle movement behaviors.