• Motion and force characteristics of wet particles in a fluidized bed were studied.
• Effects of inlet gas velocity and initial liquid content were explored.
• Effects of liquid film surface tension and viscosity were also examined.
• Liquid bridge force and inter-particle contact force were quantitatively analyzed.
• Agglomeration behavior under various parameters was investigated.
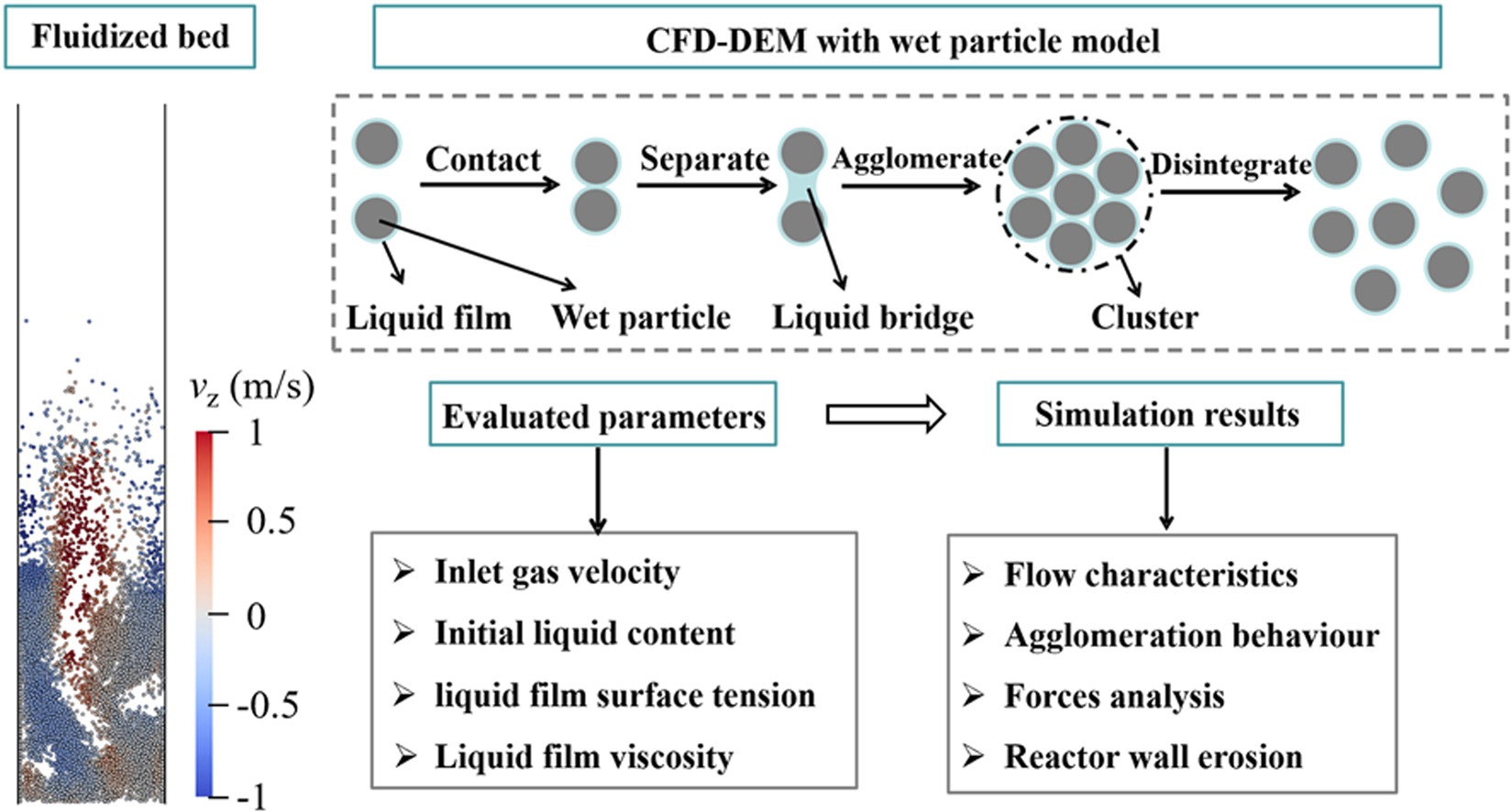
The presence of liquid alters the motion and force behaviors of wet particles compared to their dry counterparts. To investigate these differences, this study established a wet particle model using the discrete element method coupled with computational fluid dynamics. After validating the model, the fluidization behavior and force characteristics of wet particles as well as reactor wall erosion were examined, focusing on the effects of inlet gas velocity, initial liquid content, liquid film surface tension, and liquid film viscosity. The results reveal that the existence of the liquid film play an important role in particle dynamics within the bed. Higher liquid film surface tension typically enhances both the average liquid bridge force and the average inter-particle contact force. However, increasing liquid film viscosity generally strengthens the average liquid bridge force but reduces the average contact force. Additionally, the presence of a liquid film generally reduces the accumulated erosion volume of the reactor wall. These observations provide valuable insights into the motion and force behavior of wet particles in a fluidized bed.