• A new-type carbothermal reduction denitration technology for coal-fired cement kiln was introduced.
• A tube furnace experiment was conducted to study effects of components in raw meal on denitration effect.
• Influence pattern of the addition ratio of different components on NOx reduction was grasped.
• Results provided a reference for how to reasonably adjust ratio of raw meal for a better NOx reduction.
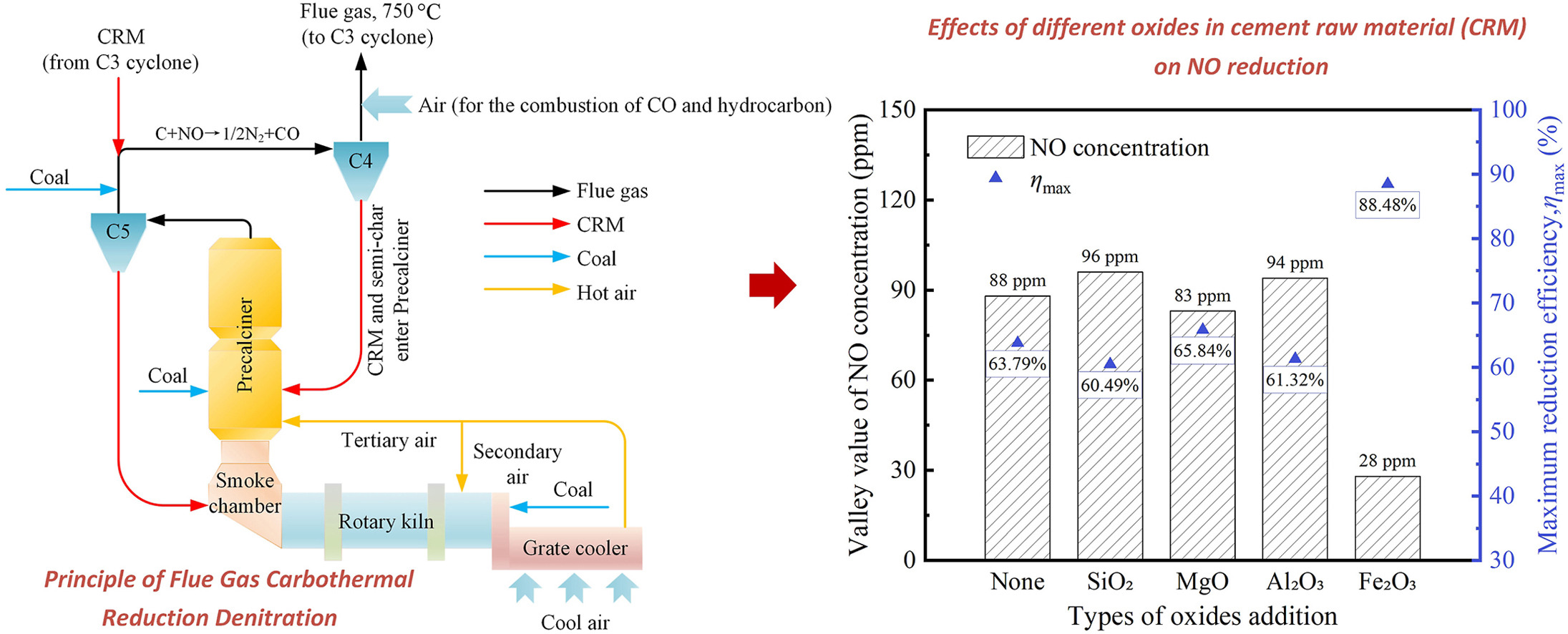
In China, the cement industry is the third largest source of NOx emissions after thermal power generation and transportation industries. Flue gas carbothermal reduction denitrification technology was proposed by the author team in previous research, and had been proved to be an effective method to cut NOx emissions from coal-fired cement kiln. Based on previous research work, a series of tube furnace experiments were conducted to further clarify the impact laws of different components in cement raw meal (CRM) on NOx reduction when using this method in the present work. Compared with the situation that only pulverized coal exists, adding only calcium carbonate had a slight inhibitory effect on NO reduction, and the maximum reduction efficiency of NO (ηmax) dropped to 63.79% from 66.67%. The addition of oxides such as SiO2, MgO, Al2O3 and Fe2O3 into the mixture of pulverized coal and CaCO3 had an impact on the reduction of NO. Overall, metal oxides promoted the reduction of NO, while SiO2 inhibited the reduction of NO. For positive promotion, Fe2O3 had the most significant effect on the reduction of NO, and ηmax reached 89.71% when the addition amount was 4% compared to 63.79% before addition. The promoting effect of metal oxides on NO reduction is: Fe2O3>MgO>Al2O3. In addition to Fe2O3, the influencing law of addition amount of MgO and Al2O3 on NO reduction had also been revealed. The outputs achieved in this study will provide a reference for how to reasonably adjust the ratio of CRM when the flue gas carbothermal reduction denitrification technology is applied into cement industry.