• LIB slurry with 0.5% amount of CB has dispersed LiCoO2 clusters and aggregated CB.
• LIB slurry with 0.5% amount of Cr has dispersed LiCoO2 particles and conductive paths.
• LIB slurry with 0.5% amount of composite conductive agent and 2:1 mass ratio of CB to Cr has an excellent network.
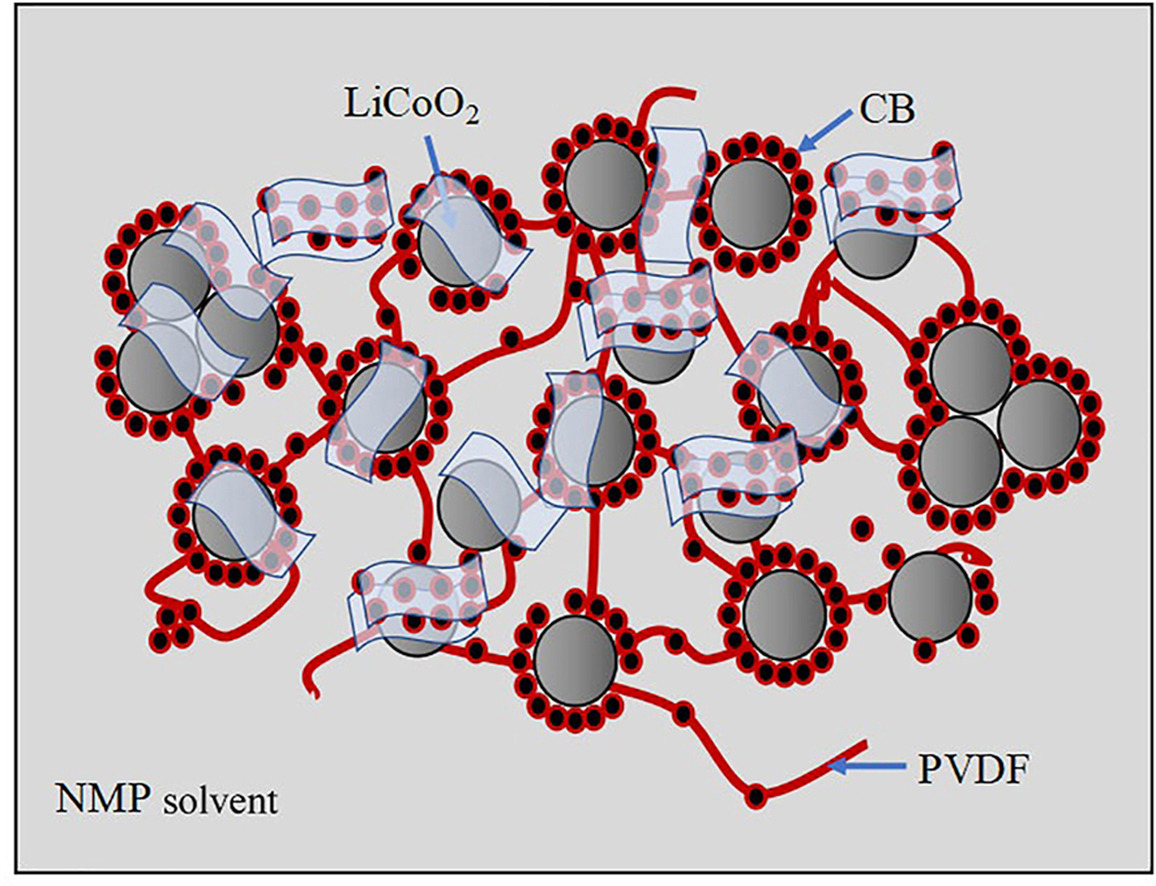
This paper clarified the network structure of the lithium-ion battery (LIB) slurry under effects of composite conductive agent amount and carbon black (CB) to graphene (Gr) mass ratio (m'CB: m'Gr). Four different amounts of composite conductive agent which are φcom1 = 0.25%, φcom2 = 0.5%, φcom3 = 0.75% and φcom4 = 1% are selected as the conductive materials for LIB slurries. Meanwhile, to discriminate the individual impacts of CB and Gr, two distinct mass ratios of CB to Gr, namely, m'CB: m'Gr = 1: 2 and m'CB: m'Gr = 2: 1, are additionally chosen. Moreover, the influence of single conductive additive agent CB or Gr with the same amount as composite conductive agent on the network structure of the LIB slurry is also investigated. Furthermore, Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Raman experiments are performed to obtain the electrochemical, morphological and Raman characterizations of LIB slurry, respectively. After analyzing the experimental results, the main conclusion shows that the synergistic interaction between CB and Gr ensures a high-level conductive efficiency because of minimizing the amount of the conductive agent and increasing the amount of LiCoO2 particles to the utmost degree, which has the potential to substantially elevating the energy density of LIB.