• First preparation of alginate microspheres using high viscosity alginate solution.
• Proposed novel microfluidic membrane emulsification technique.
• Prepared targeted alginate microspheres loaded with honokiol-doxorubicin conjugate.
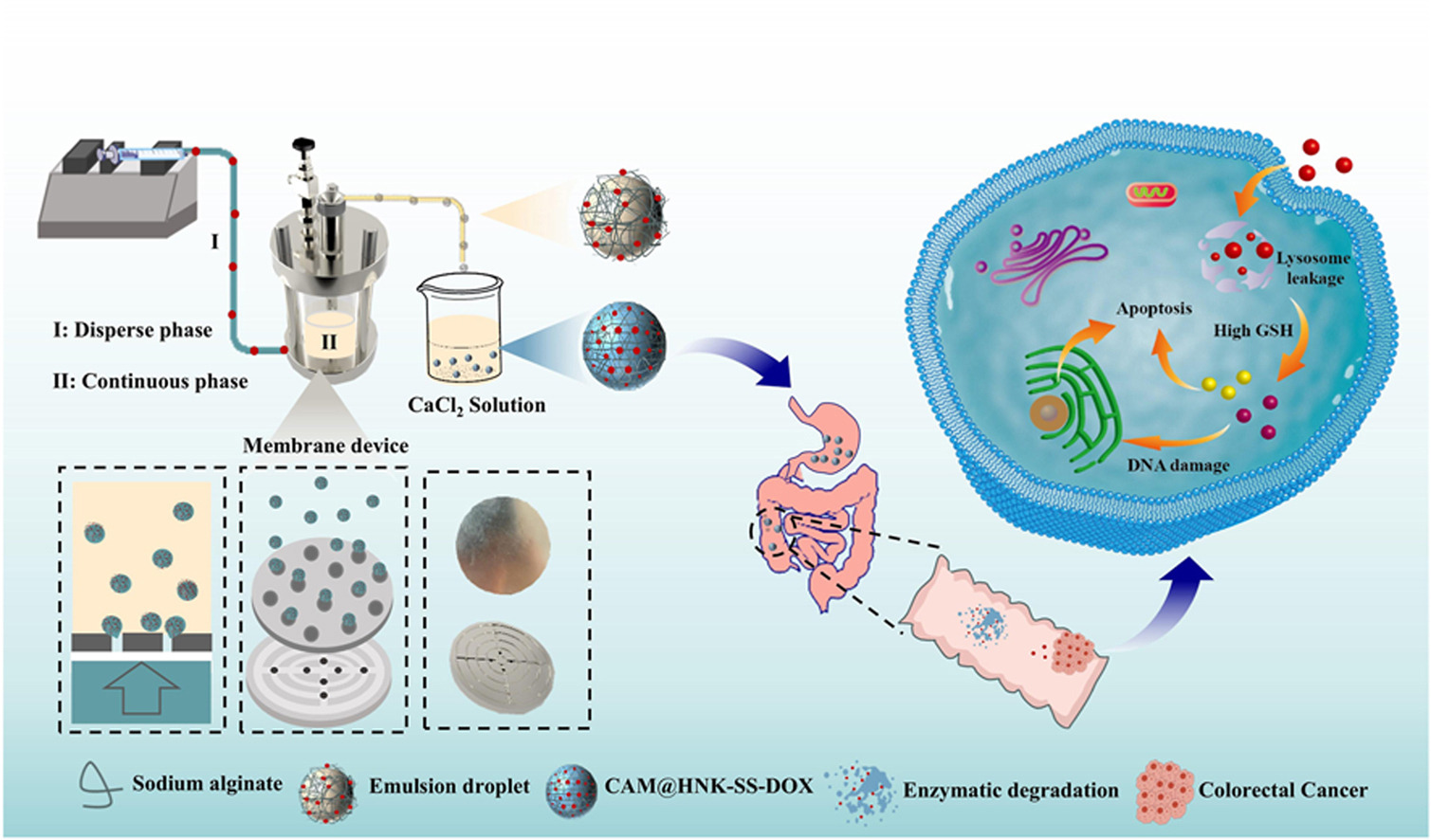
Combining drug delivery technologies with chemotherapeutic drugs is very attractive in terms of enhancing antitumor efficacy and reducing toxicity. Alginate microspheres stand out in the field of drug delivery due to their biocompatibility and high conversion rate. However, there are certain drawbacks in their preparation technology and further research is needed on how to prepare alginate microspheres with uniform particle size using high-viscosity sodium alginate solution. Therefore, this study proposed a novel microfluidic membrane emulsification technique for the preparation of alginate microspheres from high-viscosity sodium alginate solution. A tumor microenvironment-responsive colorectal cancer-targeted oral drug delivery system was constructed using a disulfide-bonded coupling of honokiol and doxorubicin as a model drug to achieve precise targeting, efficiency enhancement and toxicity reduction. The results showed that the prepared microspheres were relatively homogeneous in particle size. The in vitro model showed the high stability of the microspheres in the gastric acid environment and the colon-targeted release characteristic. And the system triggered the breakage of redox bonds and the precise release of the drug, showing good antitumor activity. This study contributes to the construction of drug delivery systems and the study of colon cancer treatment, which has a promising application.