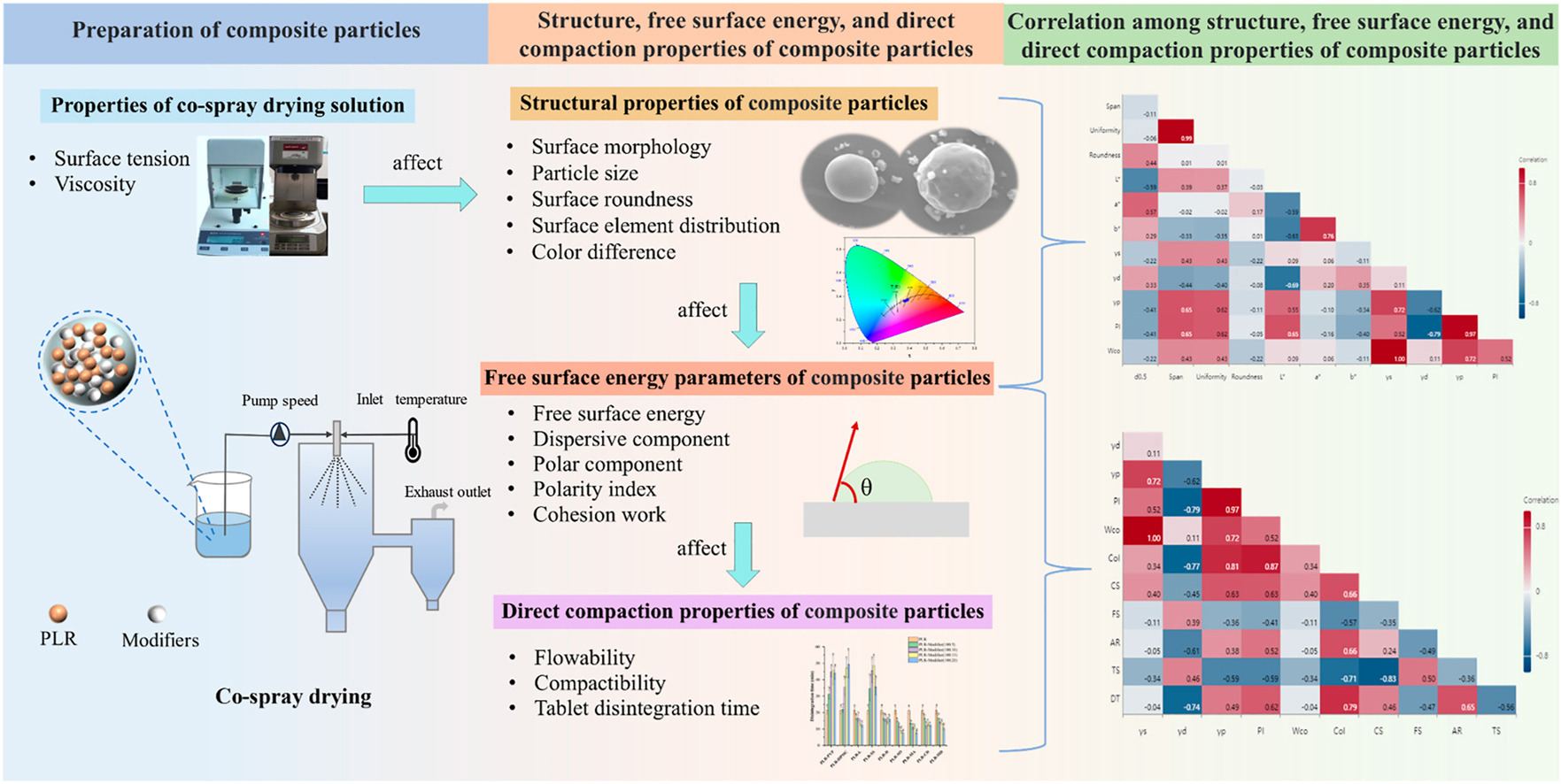
• Modifiers affect material's structure, free surface energy, and direct compaction properties.
• Correlation between structure and free surface energy parameters of material was analyzed.
• Correlation between free surface energy and direct compaction parameters of material was explored.
This study aimed to compare and analyze the effects of different modifiers on the structure, free surface energy parameters, and direct compaction properties of composite particles (CPs) prepared by co-spray drying and to explore the correlation among structure, free surface energy parameters, and direct compaction properties of CPs. CPs with Puerariae lobatae radix were prepared by adding different modifiers. The structure, free surface energy parameters, and direct compaction properties of CPs were characterized. Furthermore, Pearson correlation analysis and artificial neural network methods were used to evaluate the correlation among structure, free surface energy parameters, and direct compaction properties of CPs. The results showed that different modifiers exhibited variegated effects on the structure, free surface energy parameters, and direct compaction properties of CPs. Pearson correlation analysis showed that the particle size distribution, uniformity, and brightness were positively correlated with polar components and polarity index, with statistical significance (P < 0.01). The polar components and polarity index were positively correlated with flowability and disintegration time, and negatively correlated with compactibility, with statistical significance (P < 0.01). Overall, these findings contribute to better establishing a theoretical model among structure, free surface energy parameters, and direct compaction properties of CPs and provide a theoretical basis for predicting material properties.