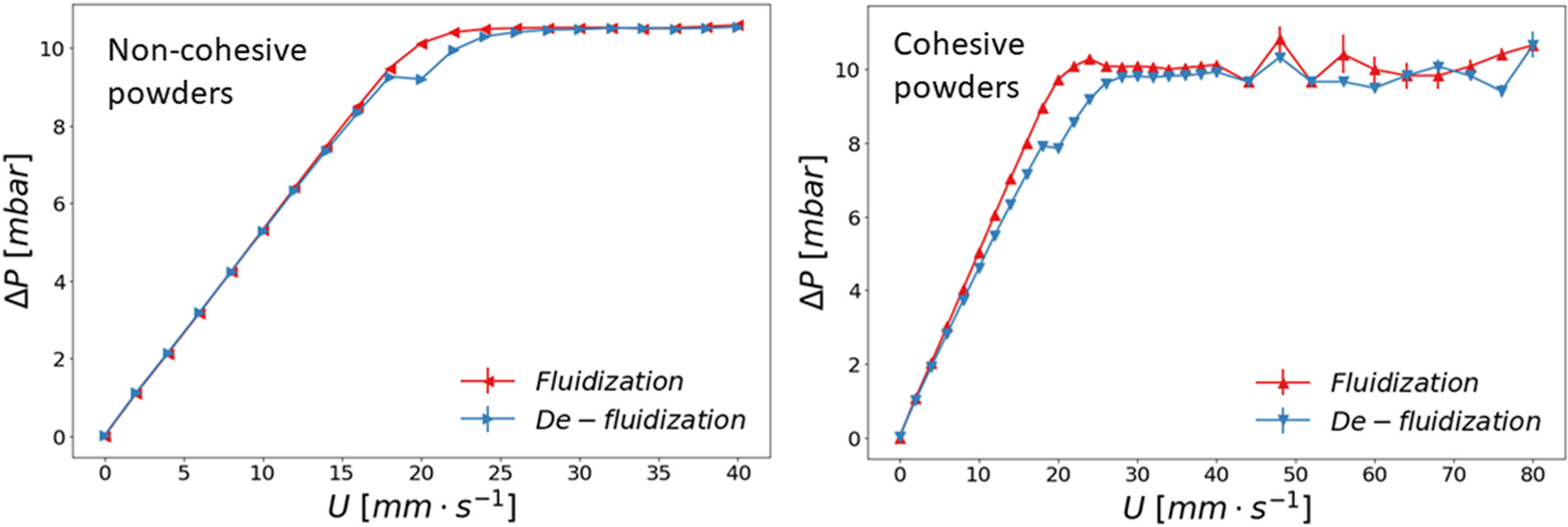
• Dry powders fluidize; wet cohesive powders do not fluidize.
• Cohesion increases hysteresis in fluidization-defluidization cycles.
• Shear stress increases with increasing cohesion.
• Shear stress and viscosity decreases with increasing fluidization index.
A virtual Couette rheometer is used to study the behavior of dry and wet granular materials in an aerated bed. A typical fluidization curve for dry powders exhibits fixed bed characterized by linear increase in pressure drop with increasing air velocity. This is followed by a fluidized bed at a constant pressure drop with further increase in air velocity. However, wet powders display different aeration behaviour due to the inhomogeneous gas flow through the bed. The fluidization behaviour of the powder upon addition of small amounts of silicon oil liquid has been tested for two different grain sizes. Different fluidization regimes are identified for wet powders with varying silicon oil saturations and grain sizes. Additionally, hysteresis effects in the fluidization and de-fluidization cycles of the materials are compared. The shear stresses and rheology of the materials under different fluidization conditions are also analyzed.