- Volumes 108-119 (2025)
-
Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volume 107
Pages 1-376 (December 2025)
-
Volume 106
Pages 1-336 (November 2025)
-
Volume 105
Pages 1-356 (October 2025)
-
Volume 104
Pages 1-332 (September 2025)
-
Volume 103
Pages 1-314 (August 2025)
-
Volume 102
Pages 1-276 (July 2025)
-
Volume 101
Pages 1-166 (June 2025)
-
Volume 100
Pages 1-256 (May 2025)
-
Volume 99
Pages 1-242 (April 2025)
-
Volume 98
Pages 1-288 (March 2025)
-
Volume 97
Pages 1-256 (February 2025)
-
Volume 96
Pages 1-340 (January 2025)
-
Volume 107
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
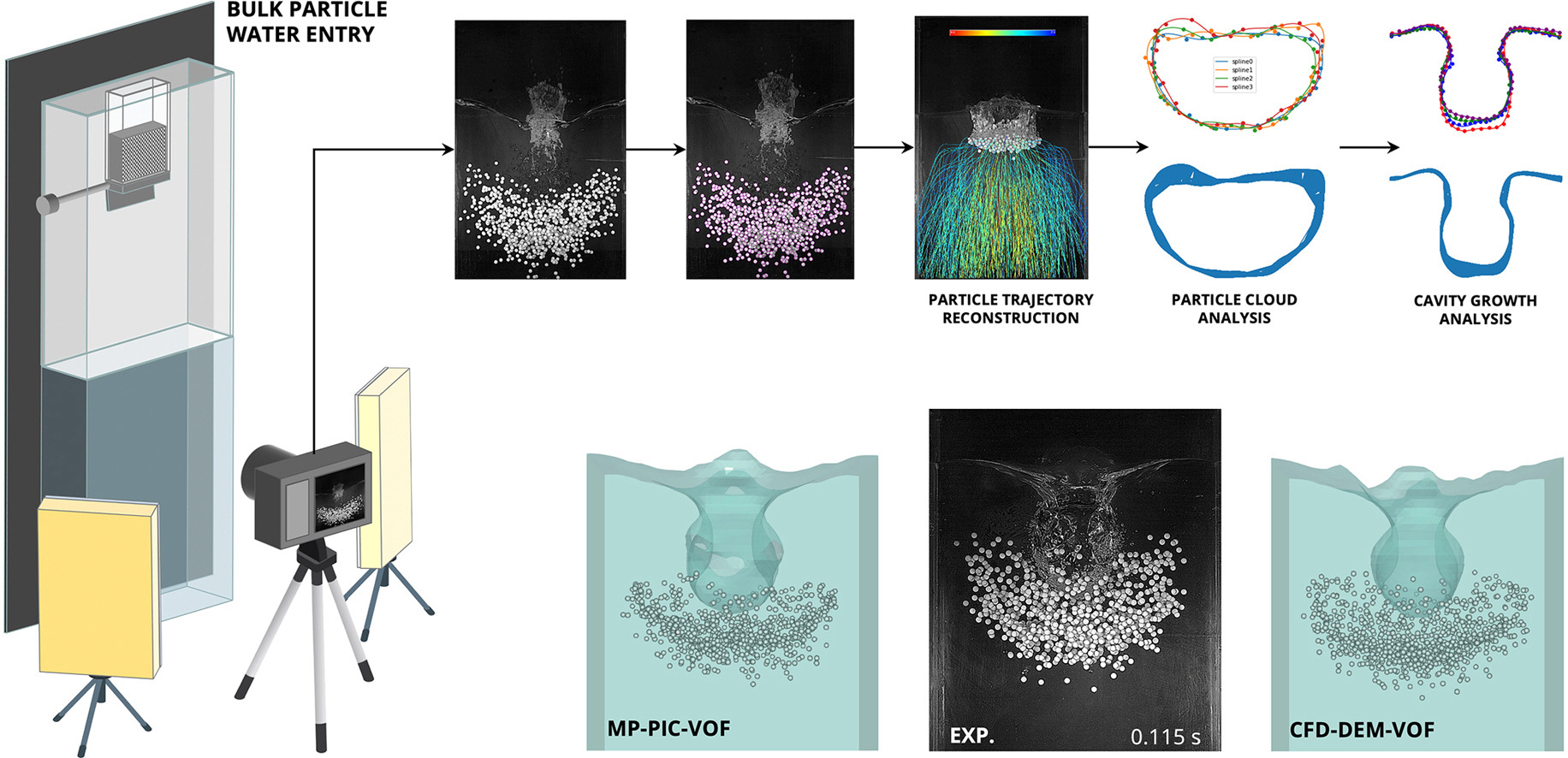
• New MP-PIC-VOF model is developed for simulation of dense solid-liquid-gas flows.
• Trilinear interpolation technique is implemented to work with unstructured meshes.
• Integration of hydrostatic pressure adaptation in the momentum equation.
• The volume-conservative alpha transport equation ensures mass conservation.
• The model is validated against experimental and CFD-DEM-VOF results.
This paper introduces the advanced MP-PIC-VOF model tailored for dense particle-laden flows with free surface, which has been developed and extensively tested across a set of validation cases found in literature and original bulk particle water entry case. A distinctive feature of the MP-PIC method is its demonstrated ability to accurately capture the behavior of closely packed particles in a fluid, even in the absence of direct pairwise particle-particle interactions. At a closed packed limit, the MP-PIC method achieves the accurate representation of the state through the resolved mean particle velocity field and implementation of the velocity limiter in the inter-particle stress force. The new model integrates a trilinear interpolation technique, specifically adapted for unstructured hexahedral meshes, and a weighted least squares method for efficient gradient computation that operates at a sub-cell level, enabling more accurate calculation of inter-particle stress gradients. Other key contributions include the integration of hydrostatic pressure adaptation in the momentum equation and a volume-conservative alpha transport equation that ensures mass conservation during the transfer of the solid phase between distinct fluid phases. The coupling framework includes a range of coupled fluid-particle forces important for particles immersed in liquid, including a dense virtual mass force. The model's validation against experimental data and CFD-DEM-VOF results focuses on key flow parameters, specifically particle velocity, dispersion profile, and cavity evolution during bulk particle water entry. The model is shown to accurately simulate complex solid-liquid-gas interactions, demonstrating its potential for optimizing a wide range of complex industrial processes such as liquid fluidized beds, solid-liquid stirred tanks, and clarifiers.